
EN 61482-2
PROTECTIVE CLOTHING AGAINST THERMAL HAZARDS FROM ARC FAULTS
The consequences of an arc fault for those affected are serious and can even be fatal in extreme cases. In the light column of the arc, the temperature briefly exceeds 9,000 degrees Celsius, which is almost twice as high as on the surface of the sun. The current reaches values of several kiloamperes (kA).
Even electric shocks of less than one hundred milliamperes (mA), as they come from a standard household socket, can be life-threatening for a person. The great heat and high currents are accompanied by a pressure wave that expands rapidly and can hurl all parts of the system and people away with its enormous force.
And the dangers don't stop there: The electromagnetic radiation from the arc fault can cause serious damage to the skin and eyes, and the toxic gases produced by the combustion can cause chemical burns and poisoning in humans.
Click here to go directly to PROTECTIVE CLOTHING ACCORDING TO EN 61482-2!

Questions and answers on EN 61482-2 (formerly IEC 61482-2)*
What is EN 61482-2?
Protective clothing that meets the requirements of this standard protects wearers against the thermal effects of a defined electric arc and prevents further burning. The clothing also protects wearers from heat. The heat may be convective, radiant, liquid metal splash or a combination of these.
What arc protection classes are there?
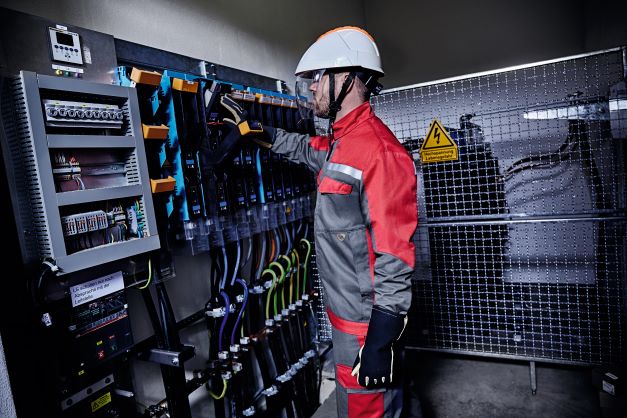

What are the test parameters for the box test?
Protection class 1:
- 0.5 seconds
- Short-circuit current: 4 kA (kiloampere)
- Electric arc energy: 158 kJ
- Impact energy: 135 kJ/m²
- 0.5 seconds
- Short-circuit current 7 kA (kiloampere)
- Electric arc energy: 318 kJ
- Impact energy: 423 kJ/m²
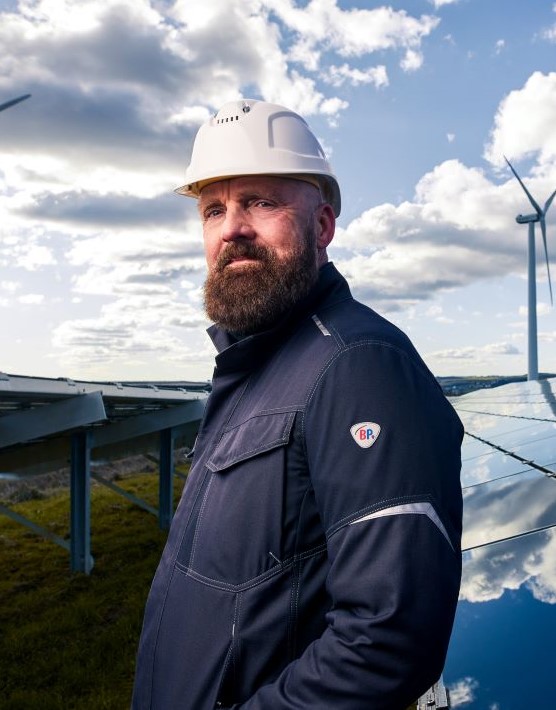

What is the protective effect of EN 61482?
What are the areas of application of the EN 61482-2 standard?
The EN 61482-2 standard primarily relates to occupational safety in the electrical industry: The standard is particularly relevant for working environments in which electricians, electrical engineers or other professionals work in the vicinity of electrical systems that harbour the risk of an arc flash.
Typical industries for this are:
- Utilities & Public Utilities,
- Electrical installation, electrical trades, electroplating,
- processing industry,
- transport of hazardous goods,
- chemical industry,
- plant construction, mechanical engineering,
- solar plants, wind turbines,
- combined and network fitters.
Box test according to EN 61482: What happens when an electric arc fault occurs?
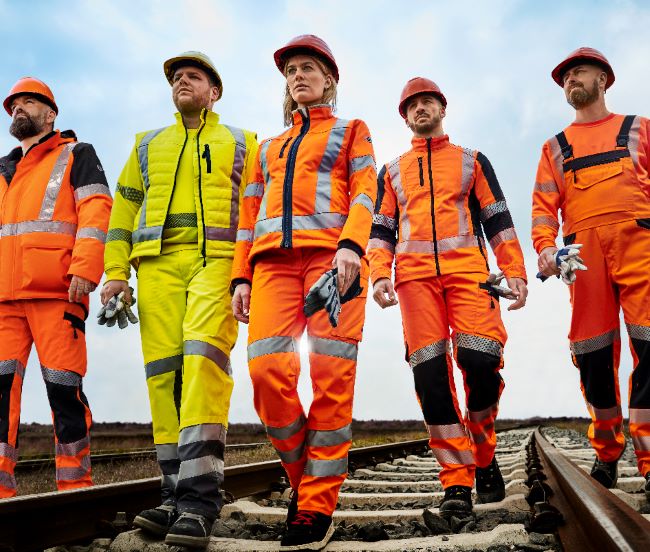
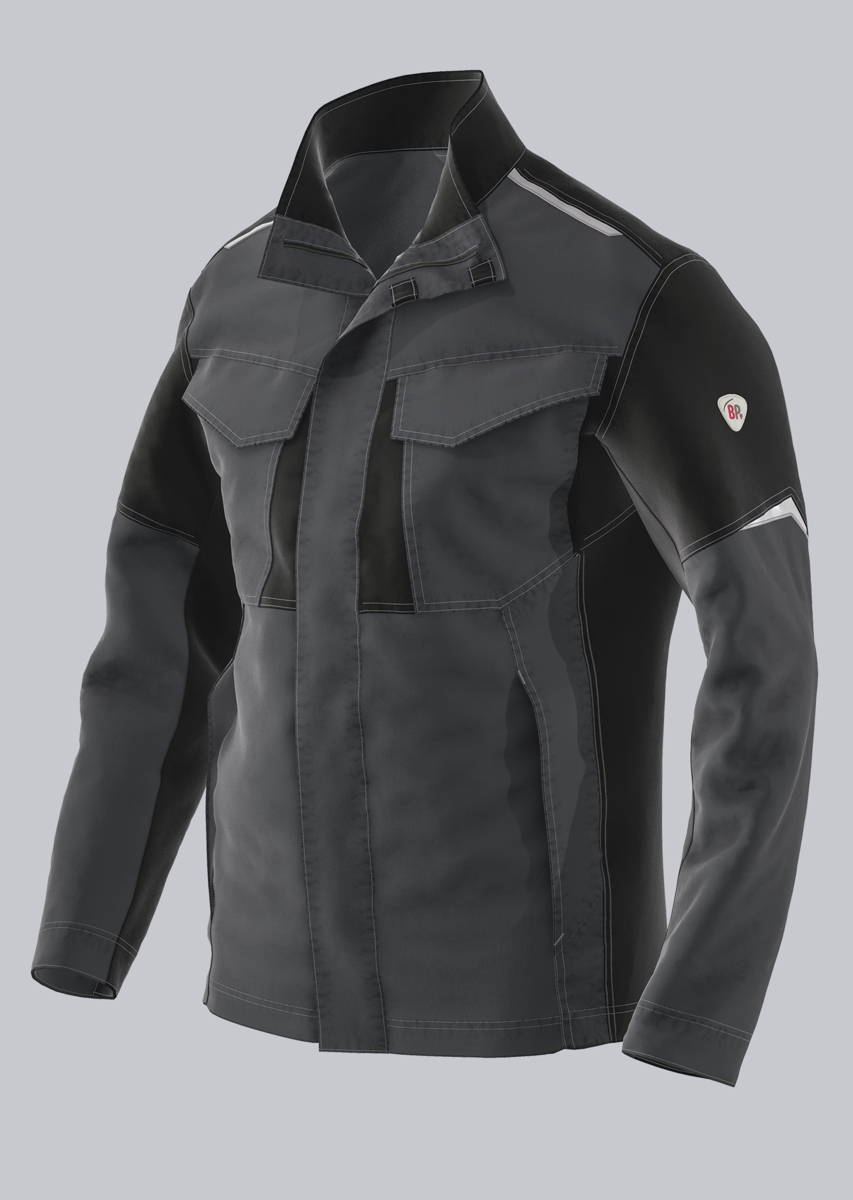
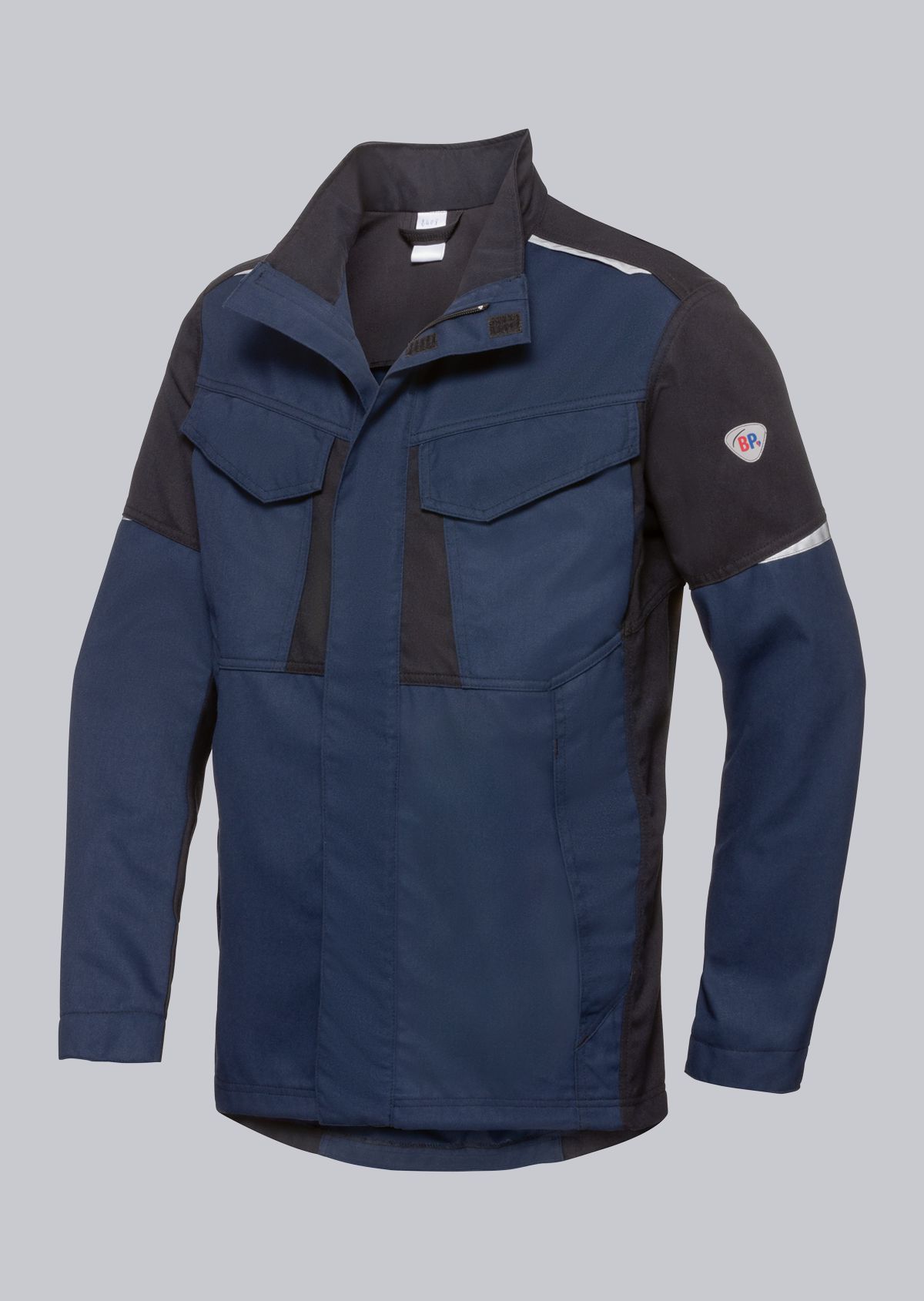
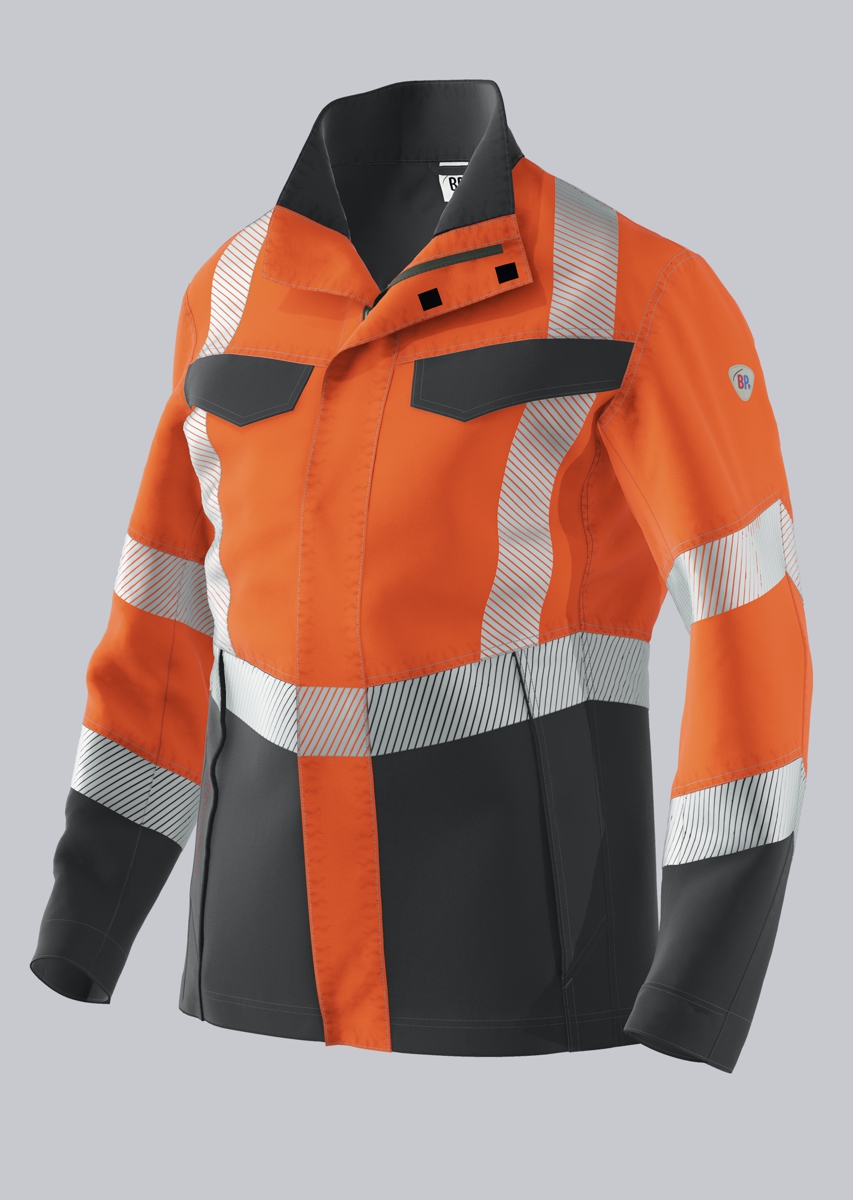
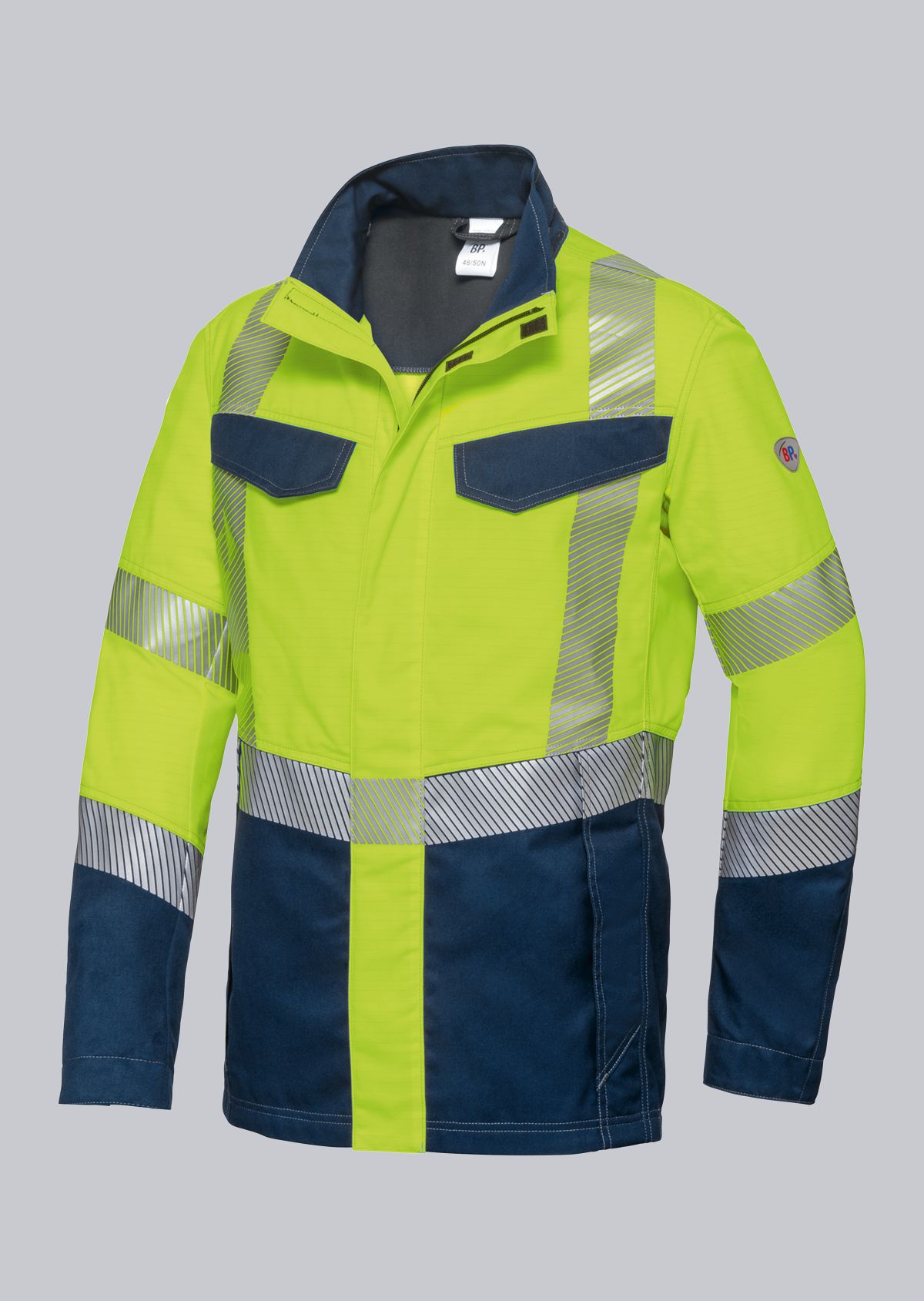
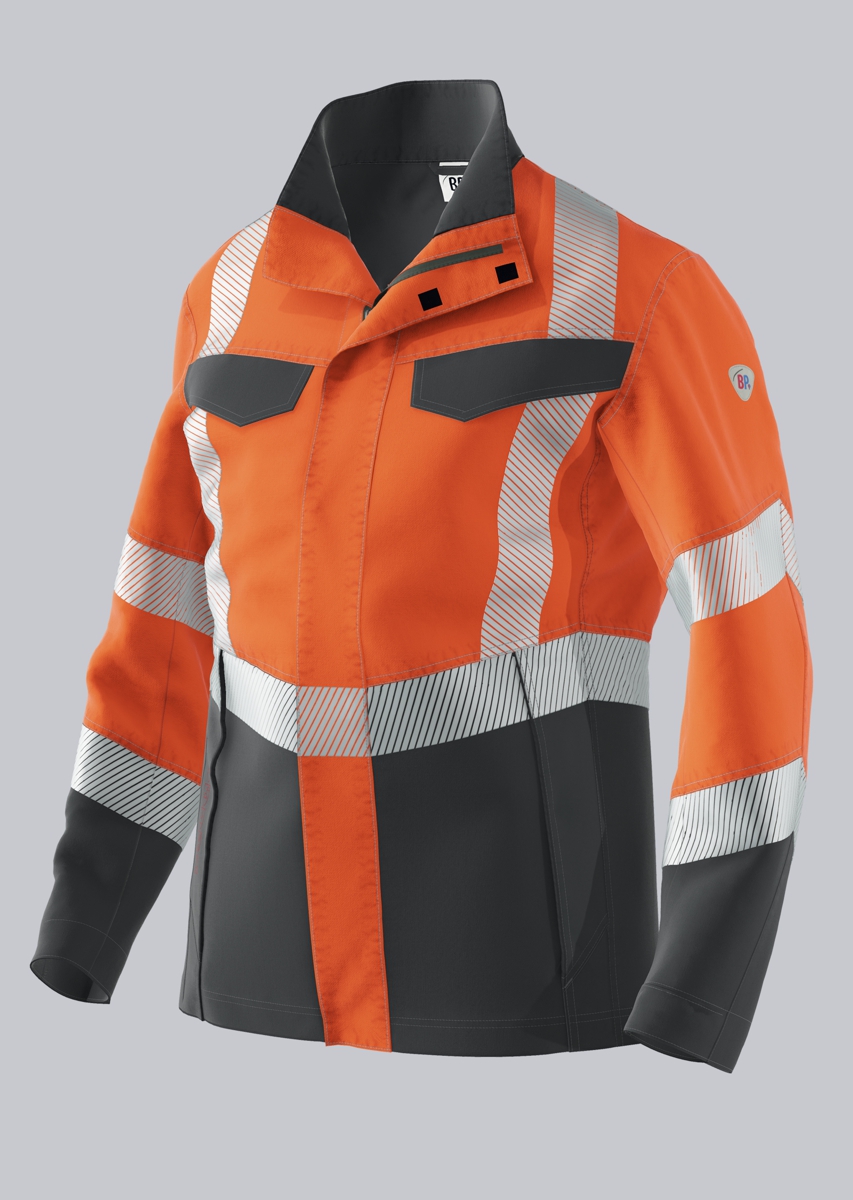
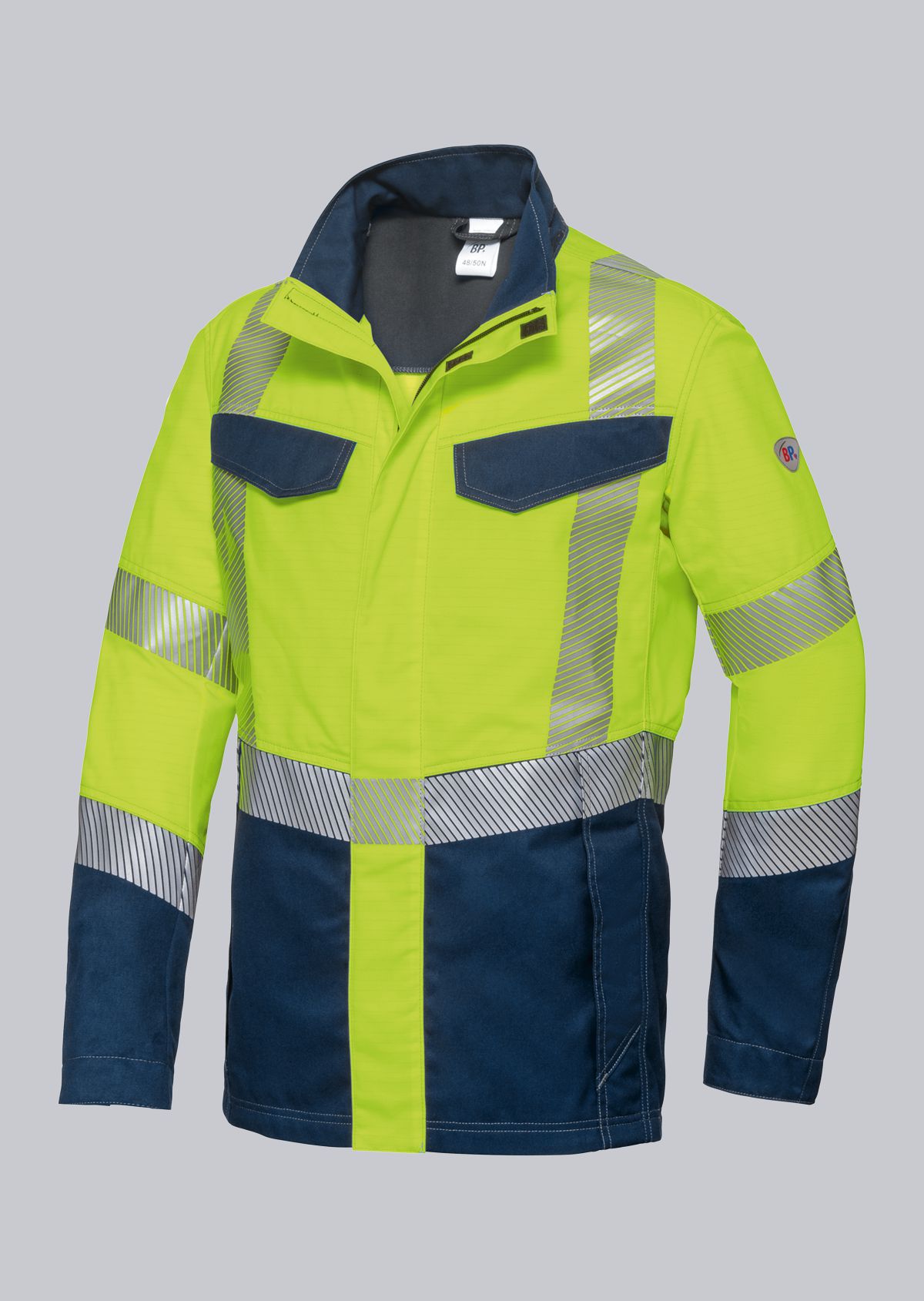
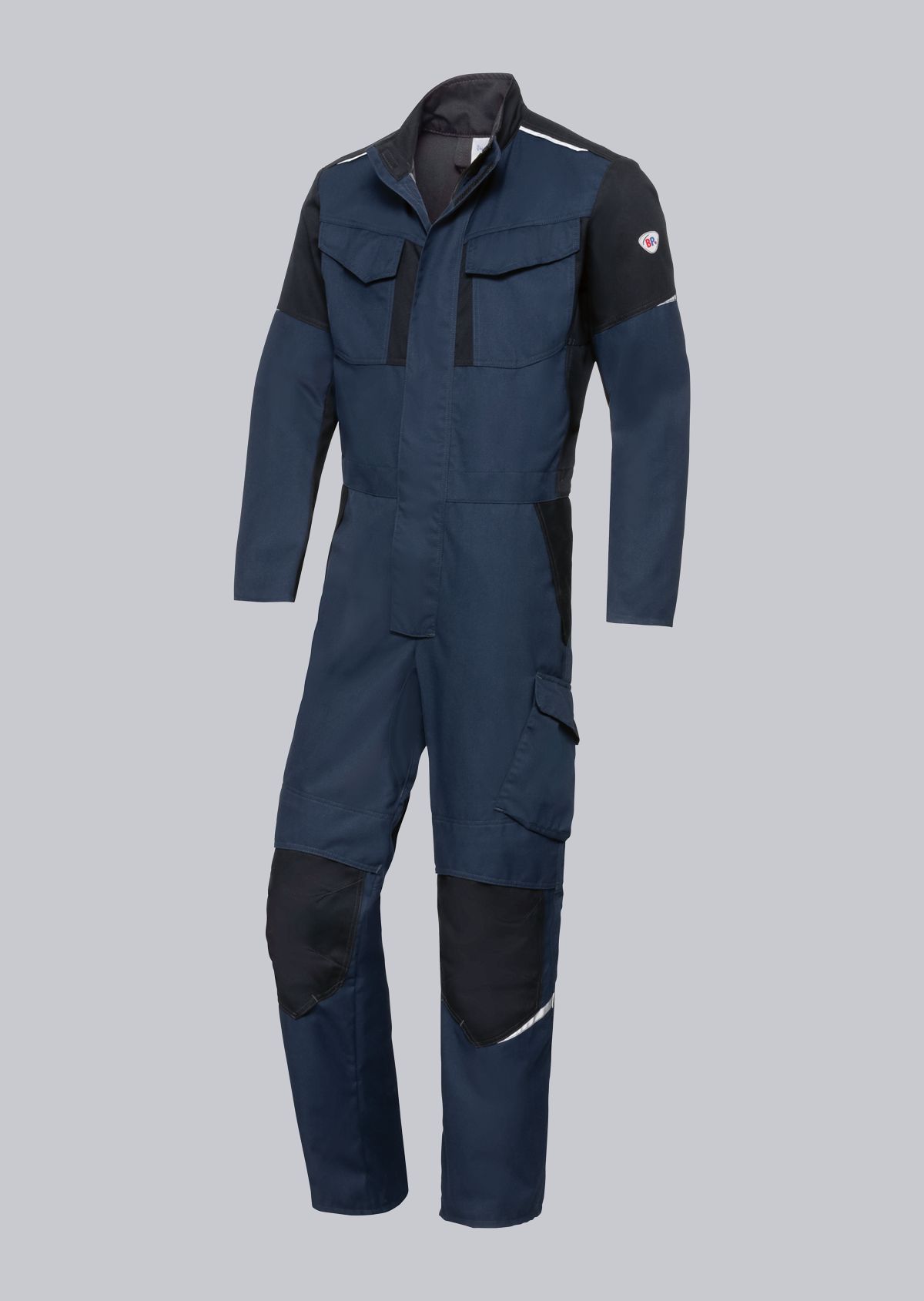
Work jackets according to EN 61482-2
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective clothing here.
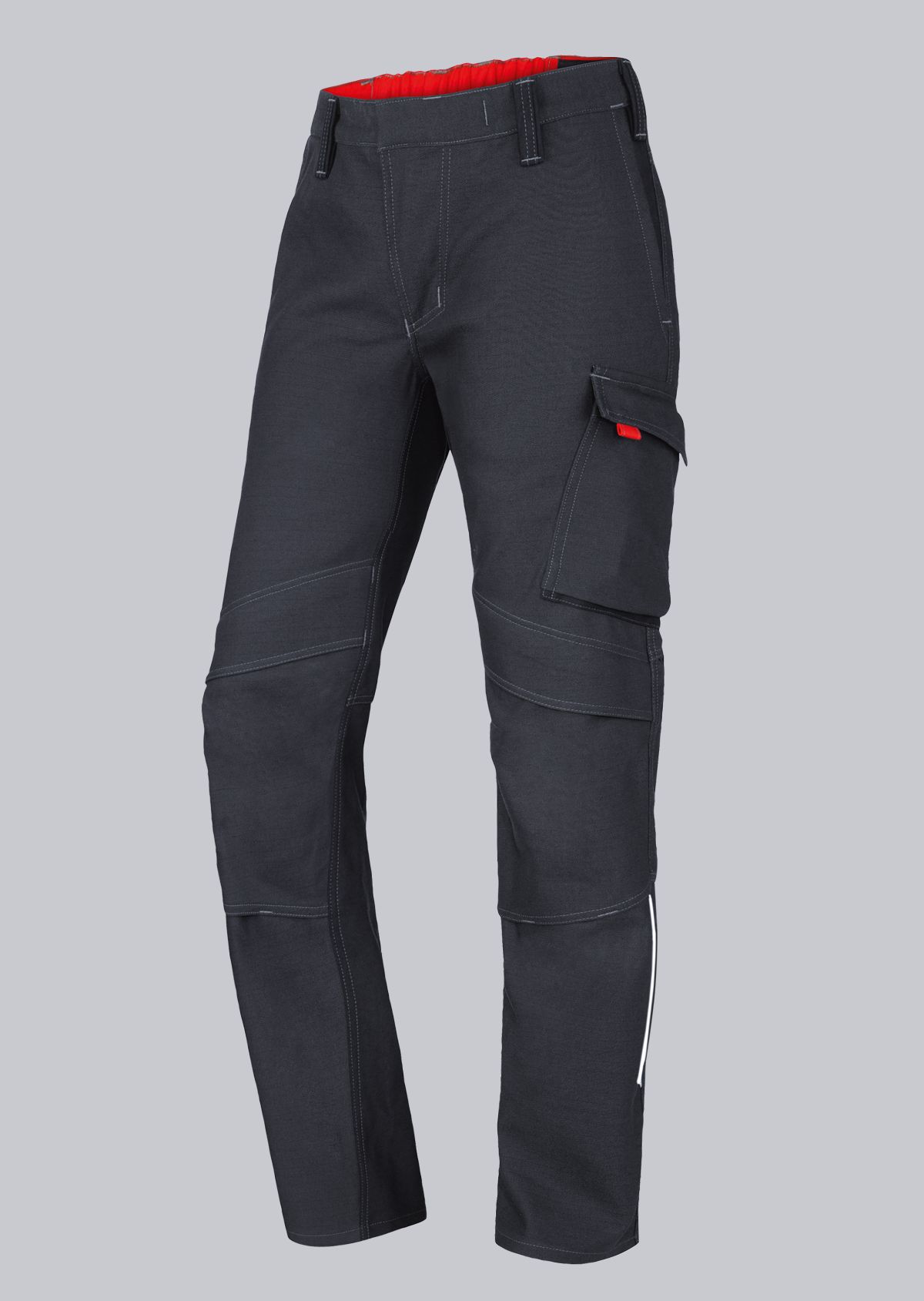
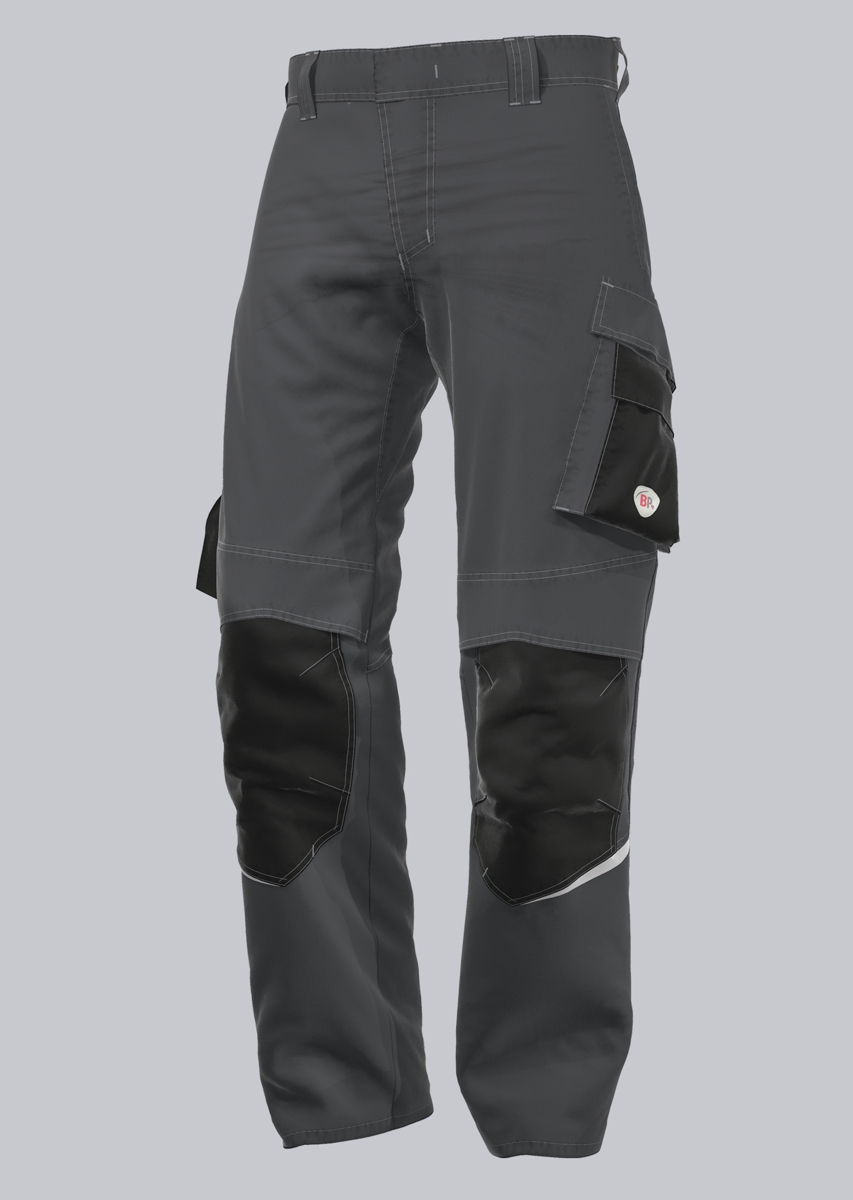
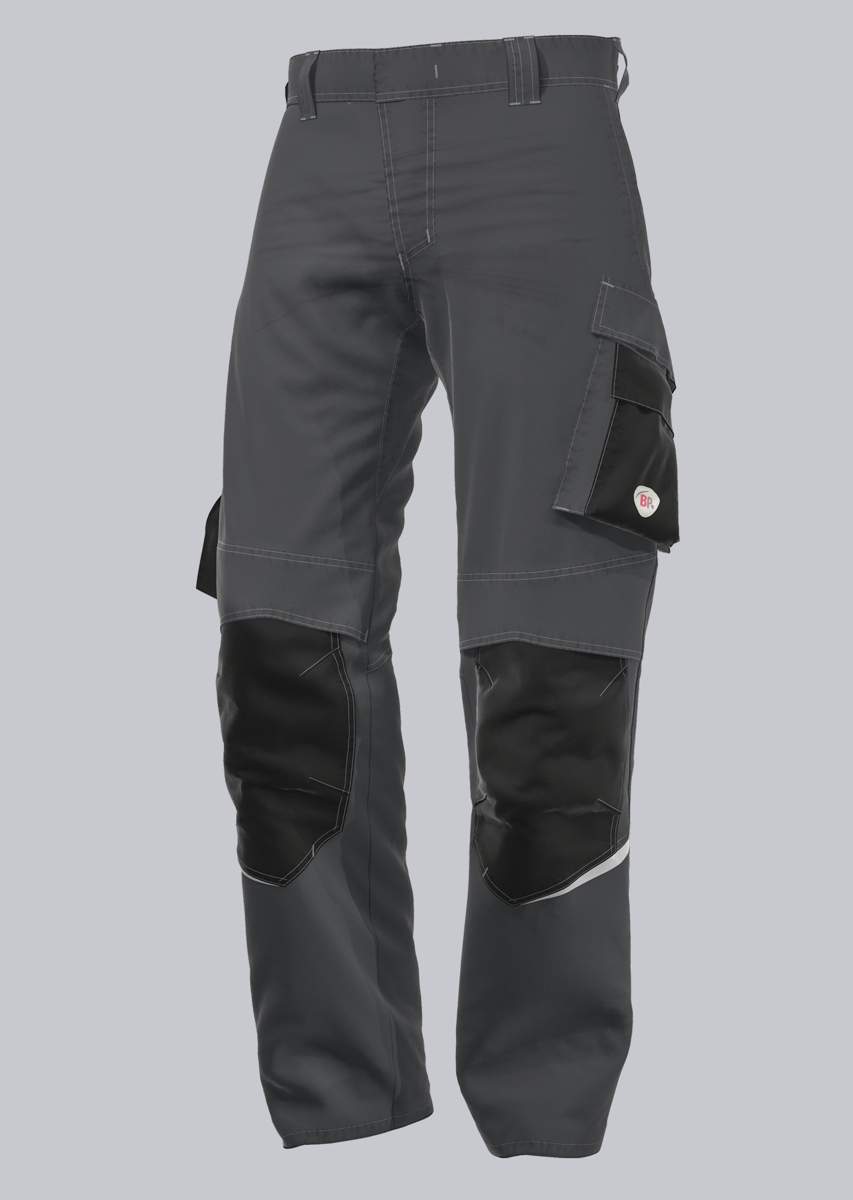
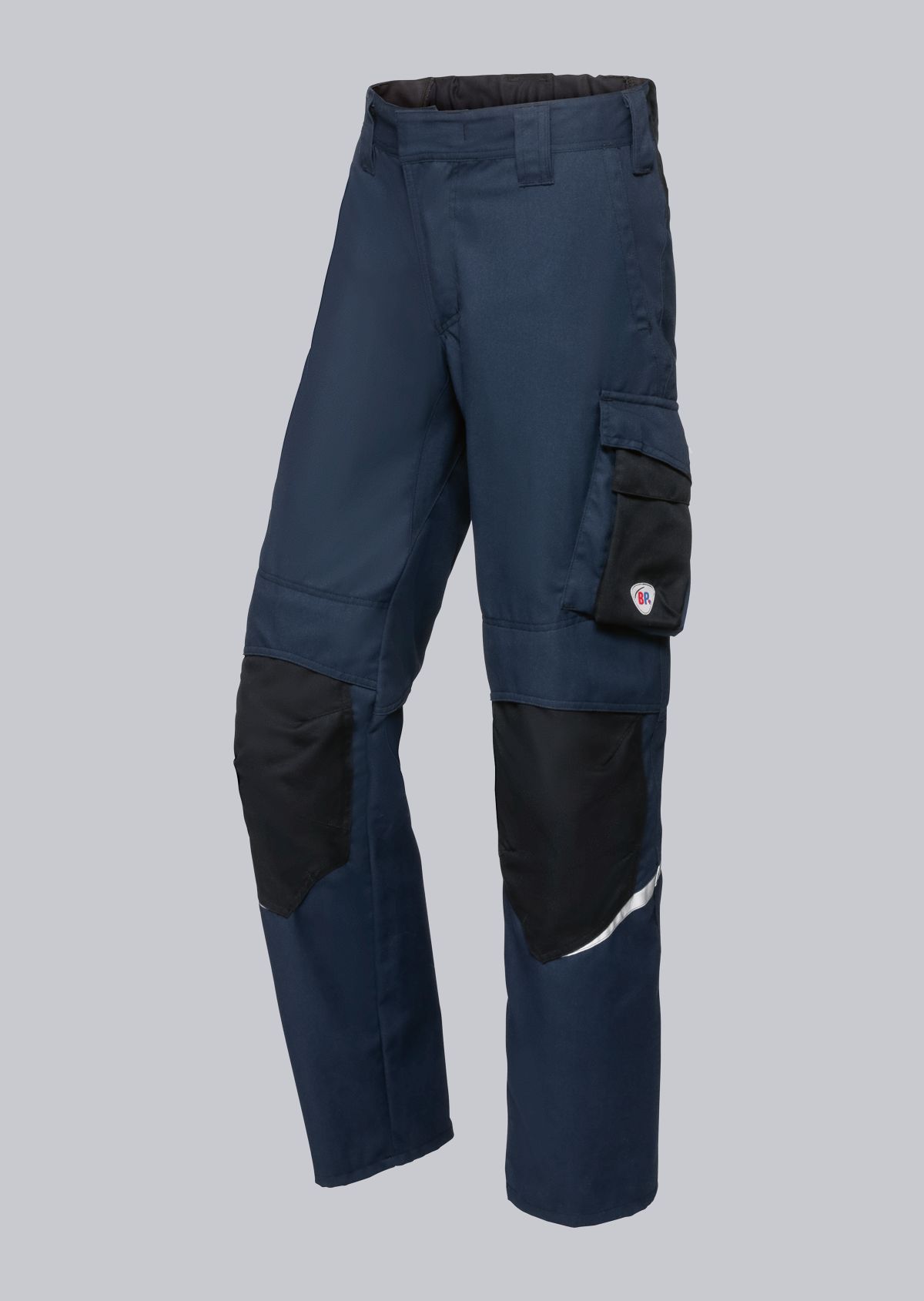
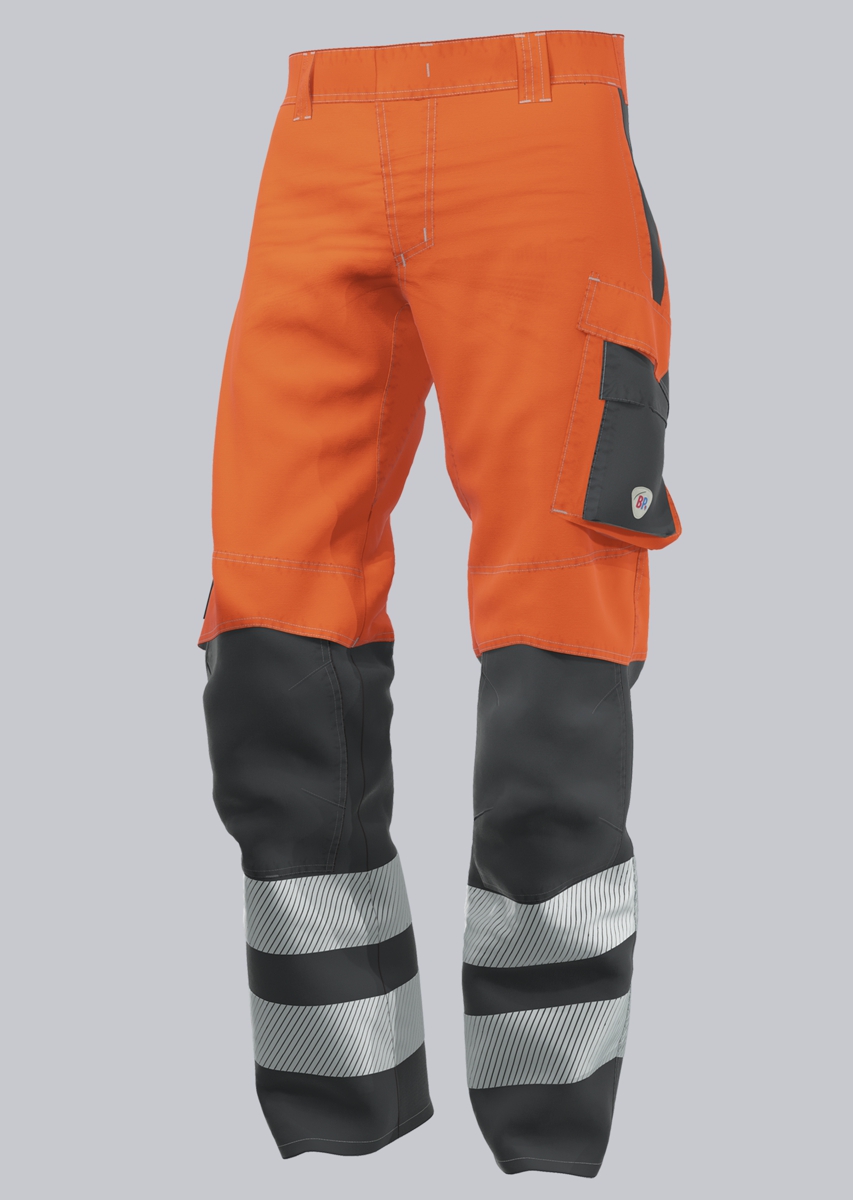
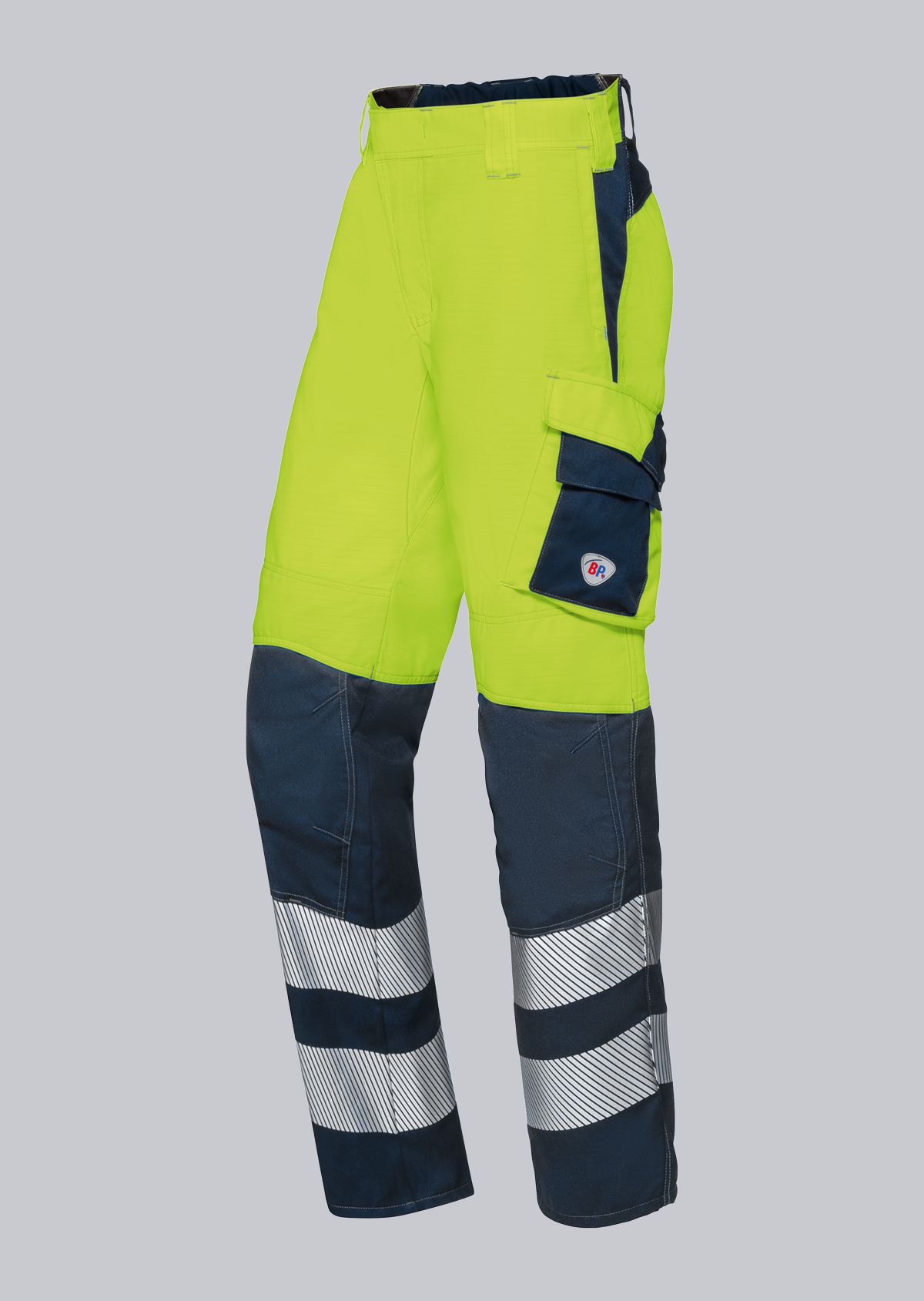
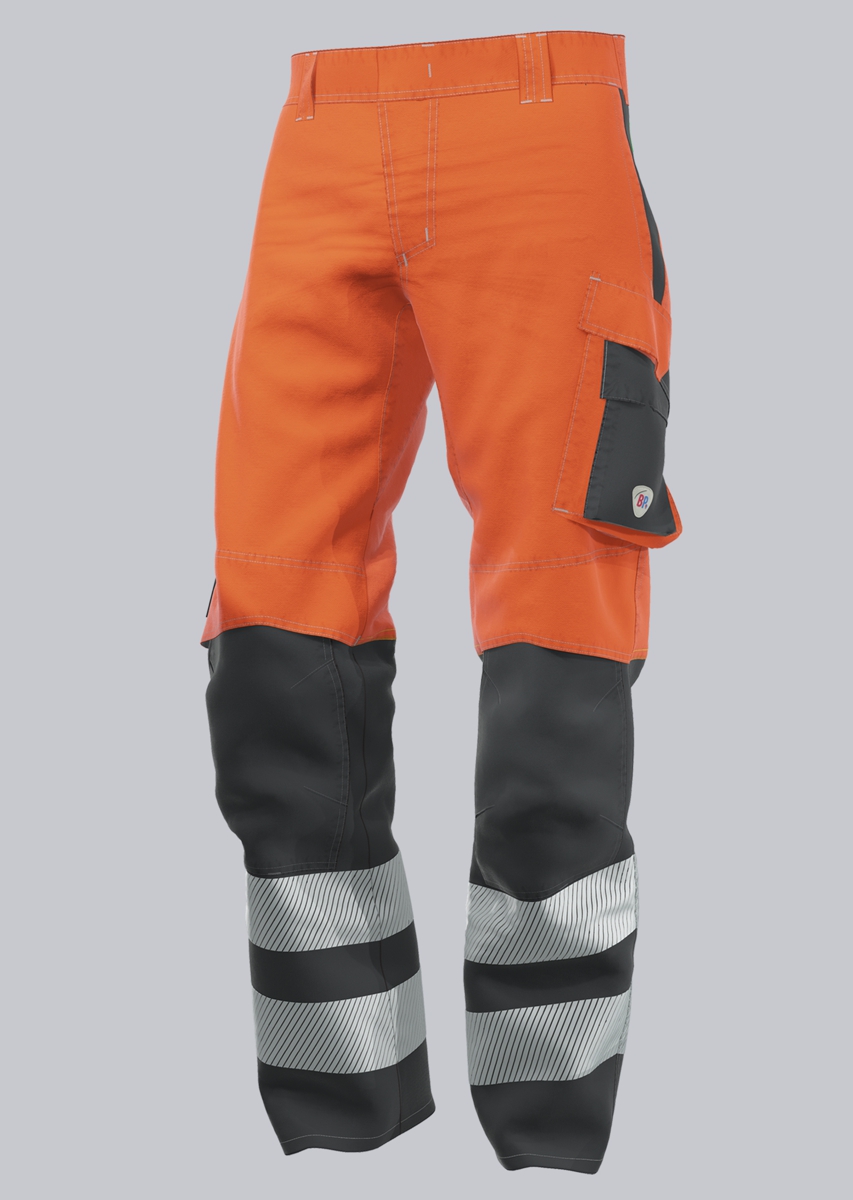
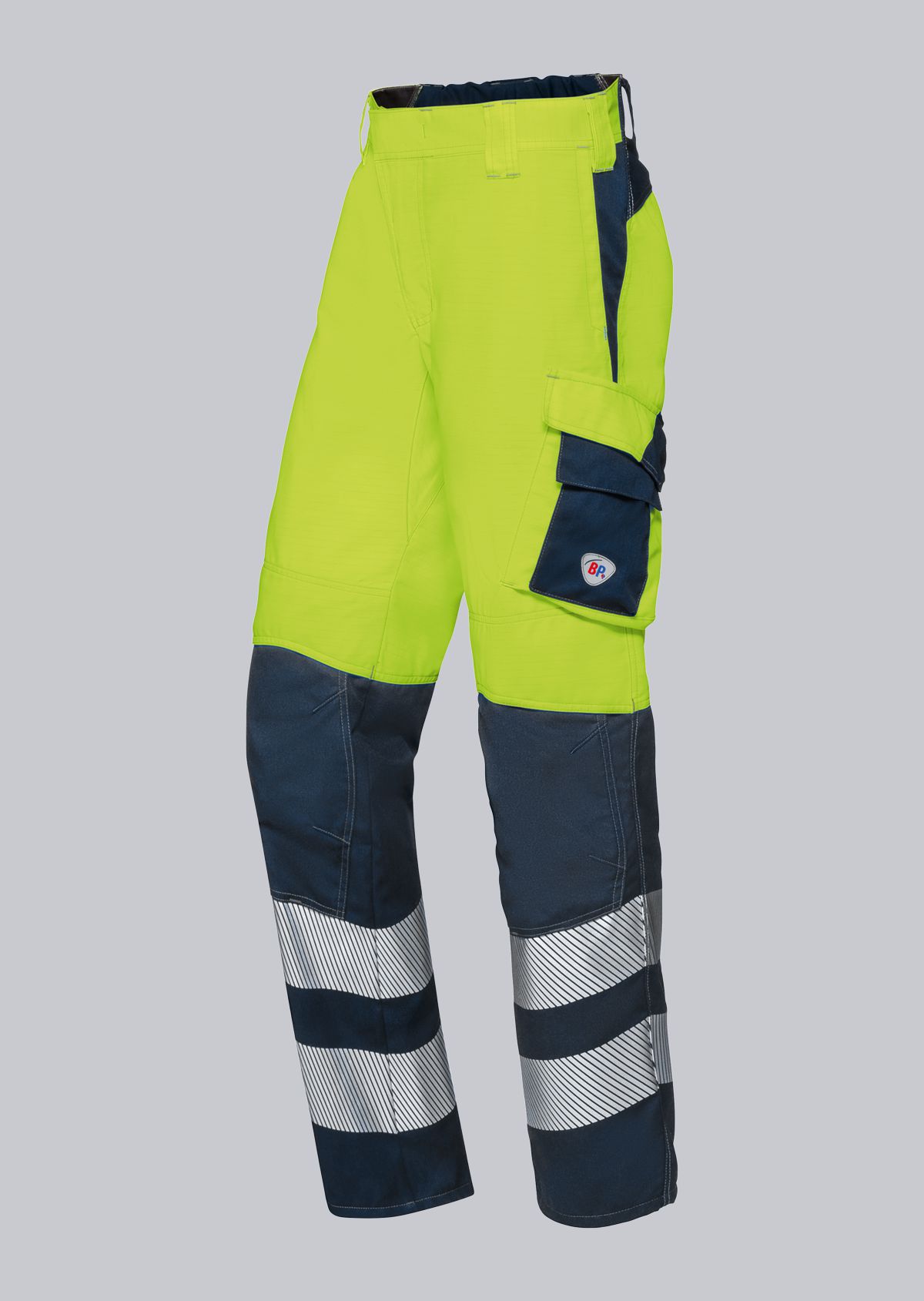
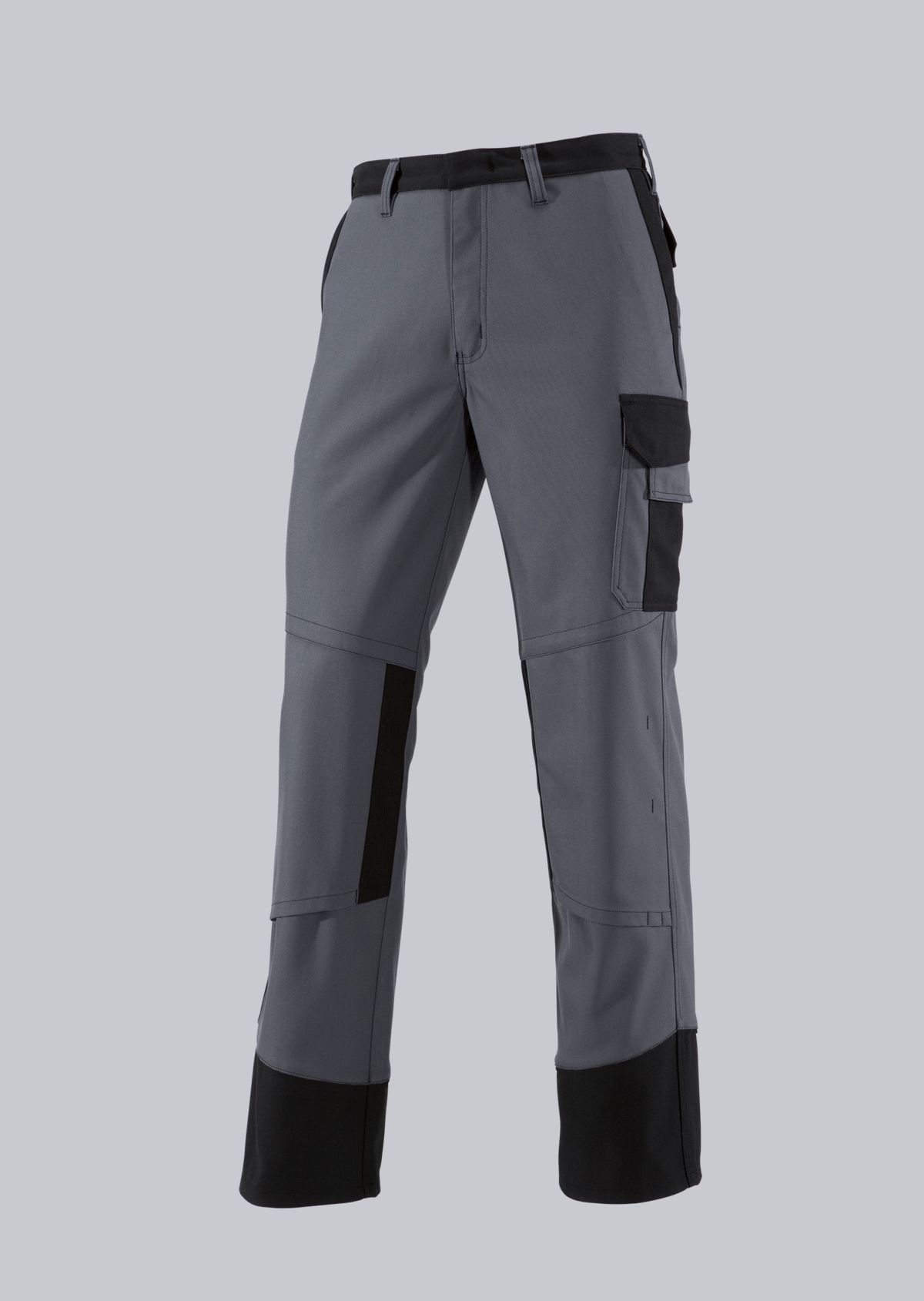
Work trousers according to EN 61482-2
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective clothing here.
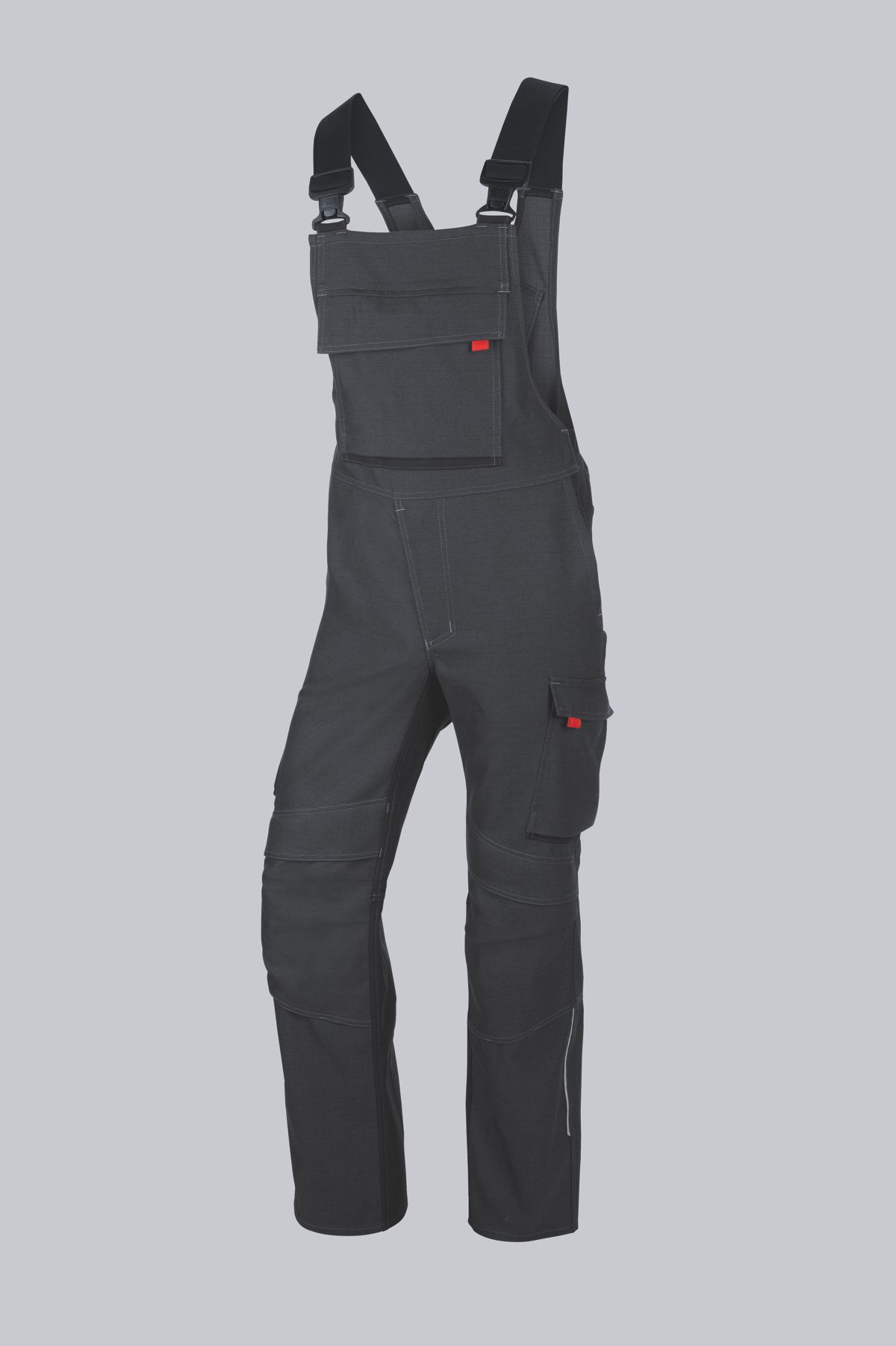
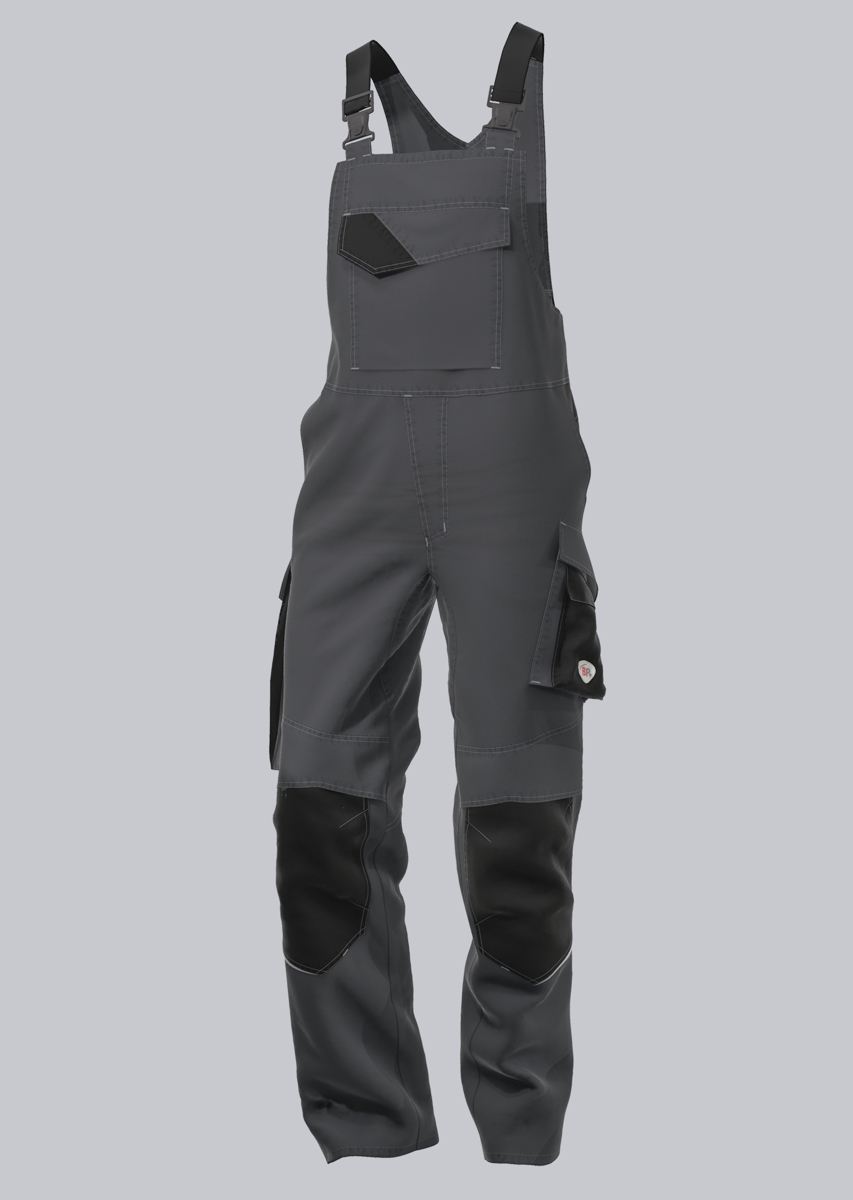
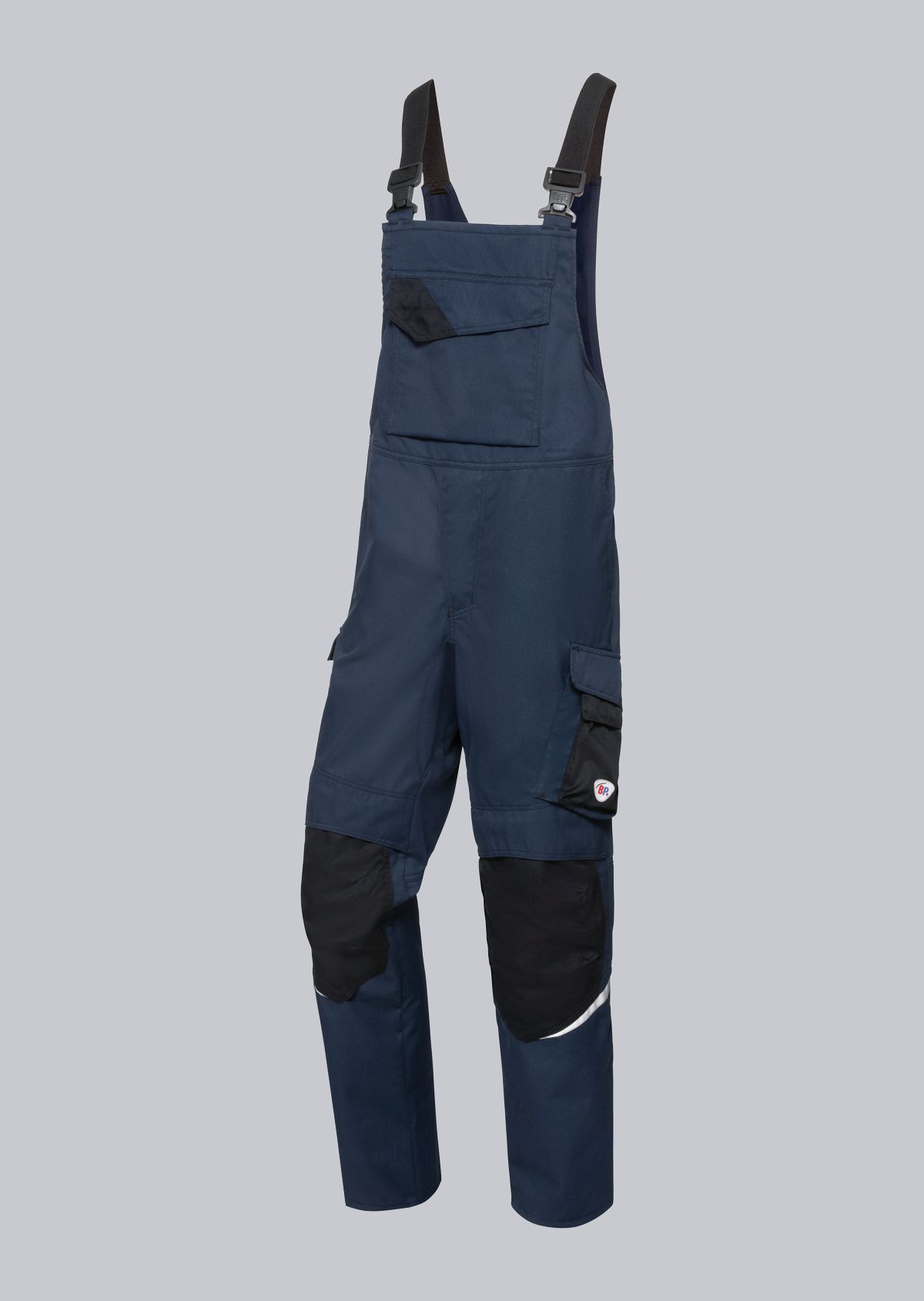
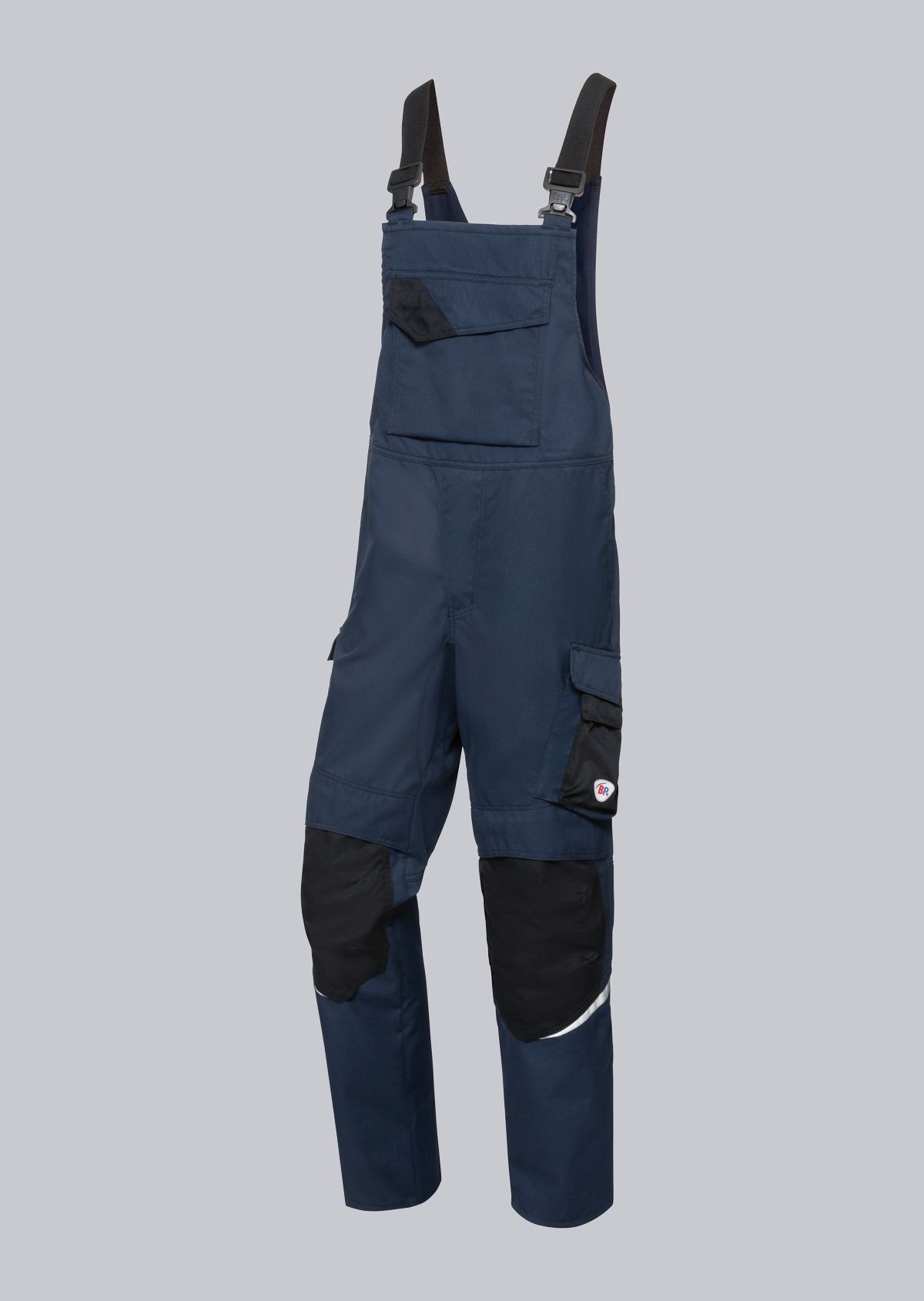
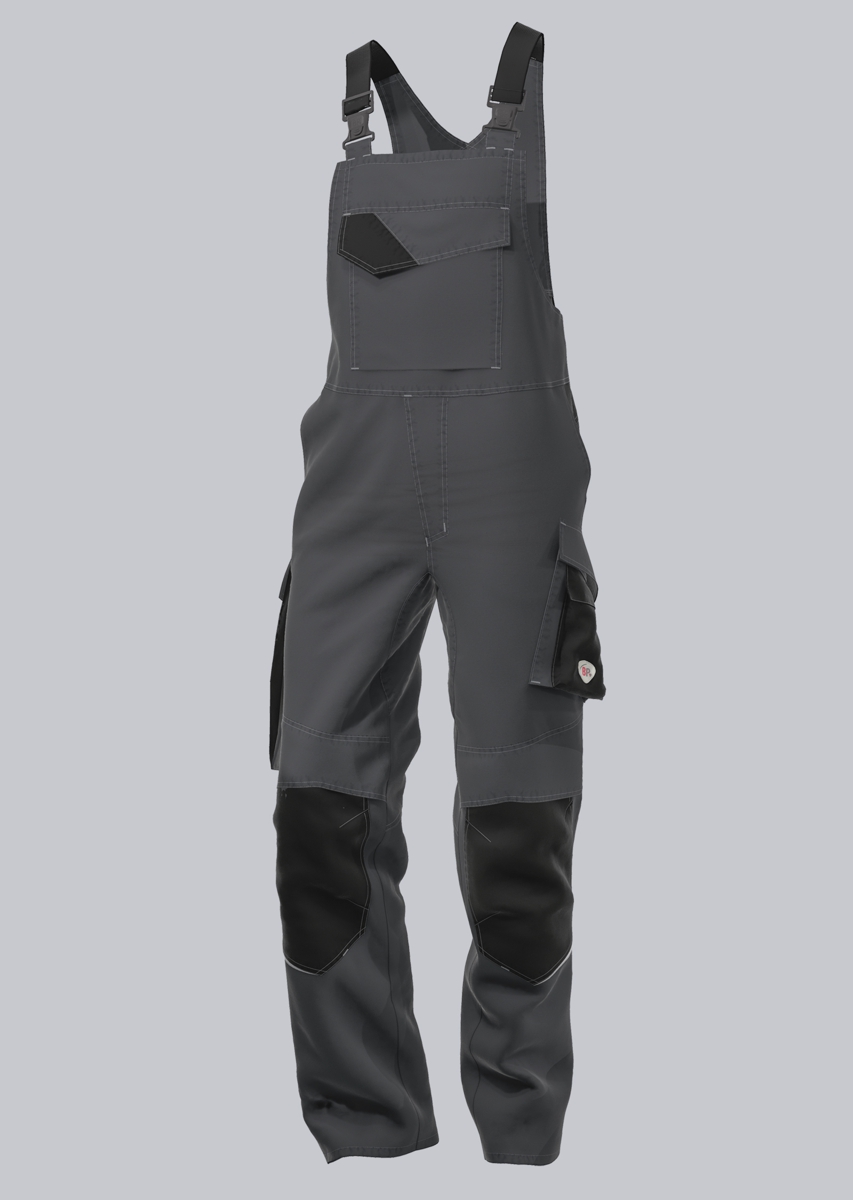
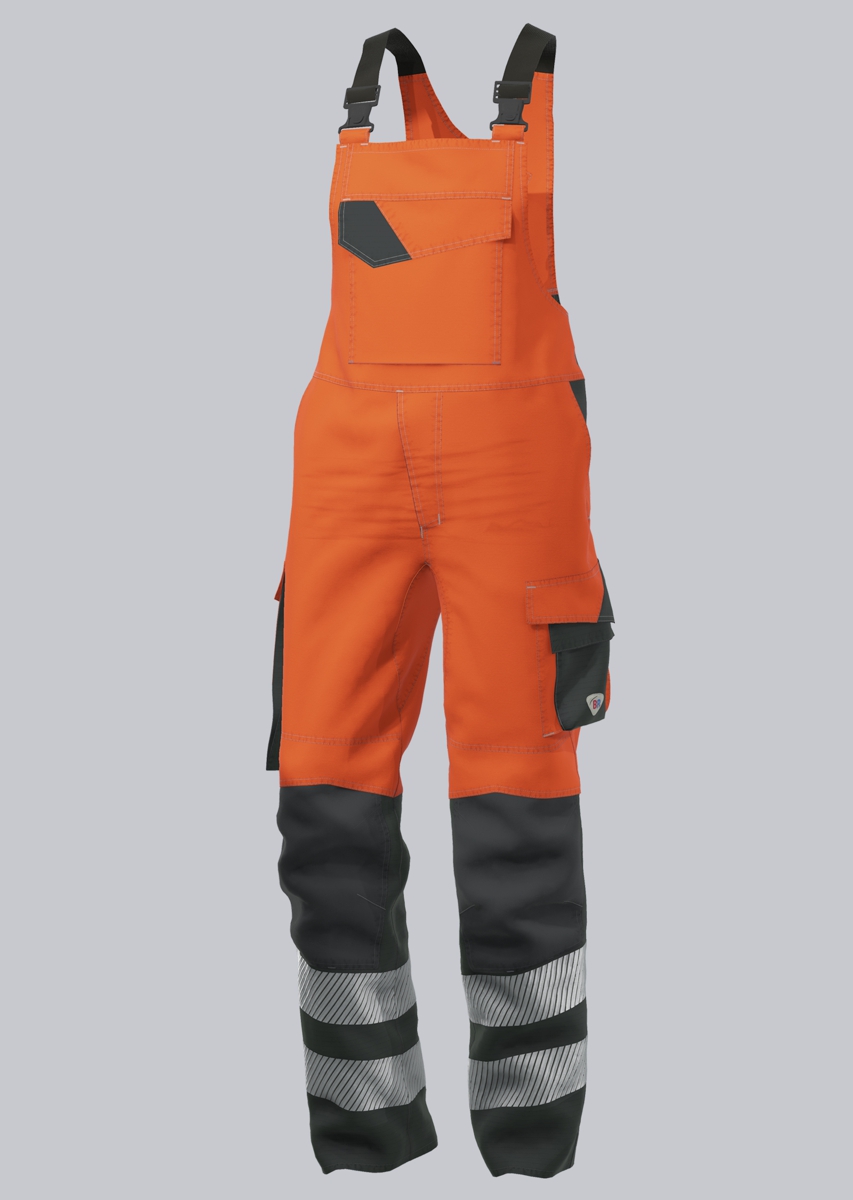
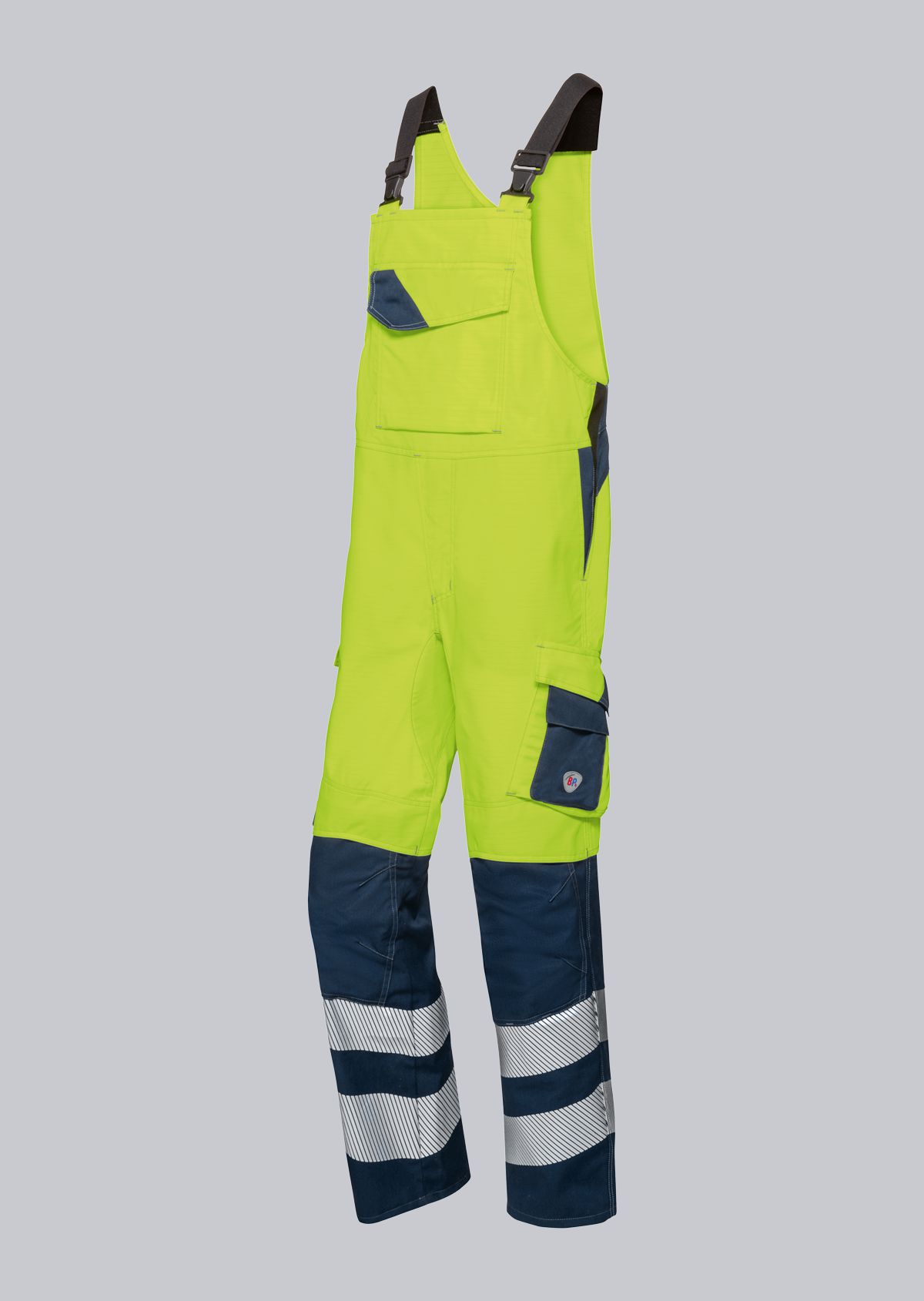
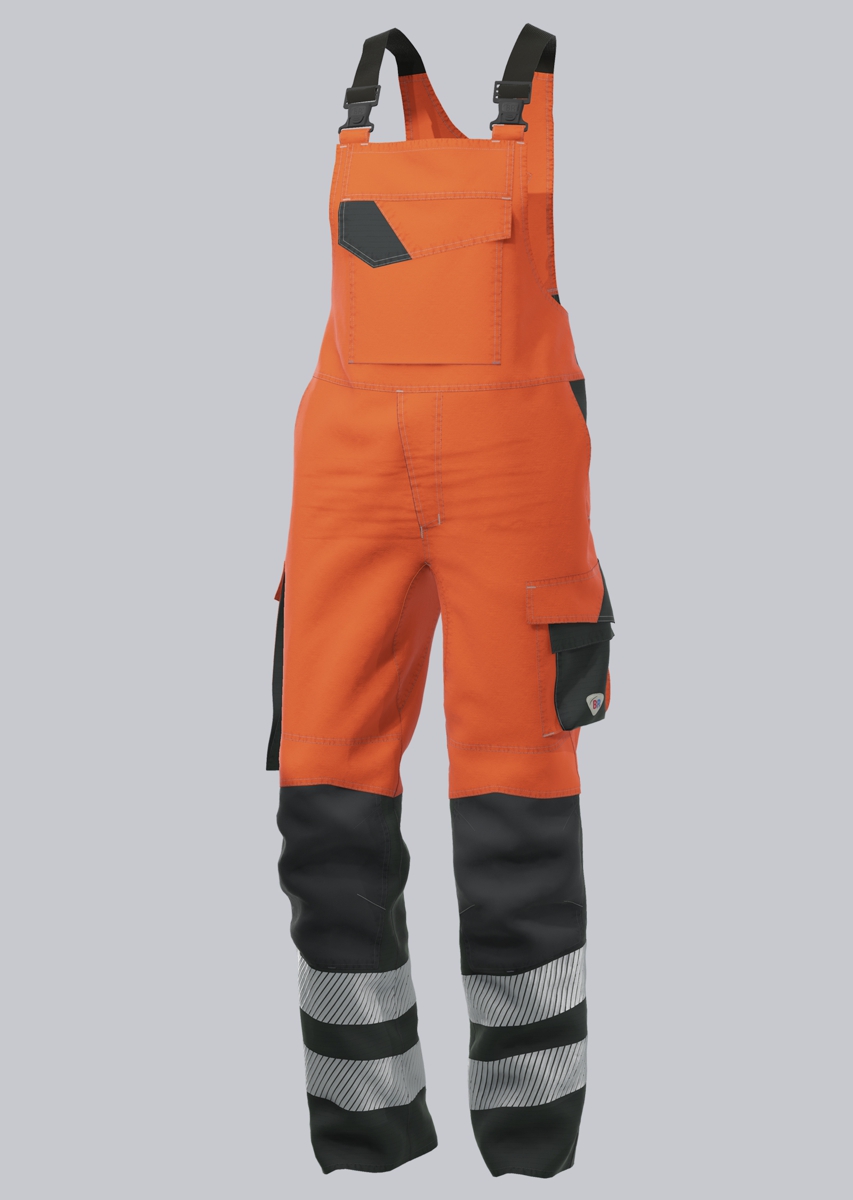
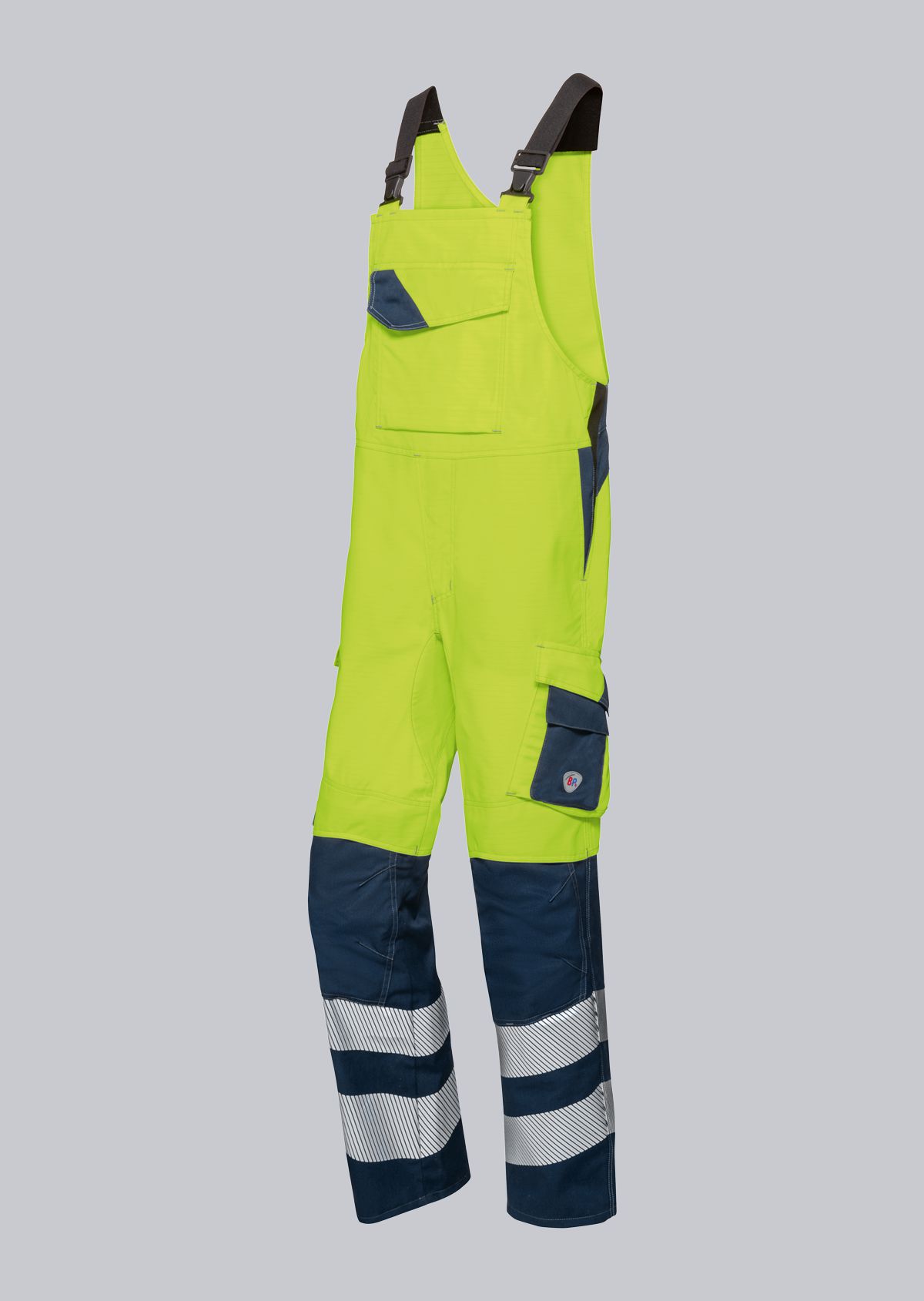
Bib & Braces according to EN 61482-2
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective clothing here.

































.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)