
EN 14058
CLOTHING FOR PROTECTION IN COOL ENVIRONMENTS
Protective clothing in accordance with the EN 14058 standard plays a crucial role in the working environment, especially in cool working areas where protection against cold and other environmental influences is of paramount importance. The EN 14058 standard specifies requirements for protective clothing specifically designed for use in cool environments.
This standard not only serves to protect the wearer from the negative effects of low temperatures, but also takes into account factors such as comfort, freedom of movement and breathability. In the following, we will take a closer look at the requirements and properties of protective clothing according to EN 14058 and highlight the importance of this standard for working environments where protection in cool environments is crucial.
Click here to go directly to cold protection clothing according to EN 14058!
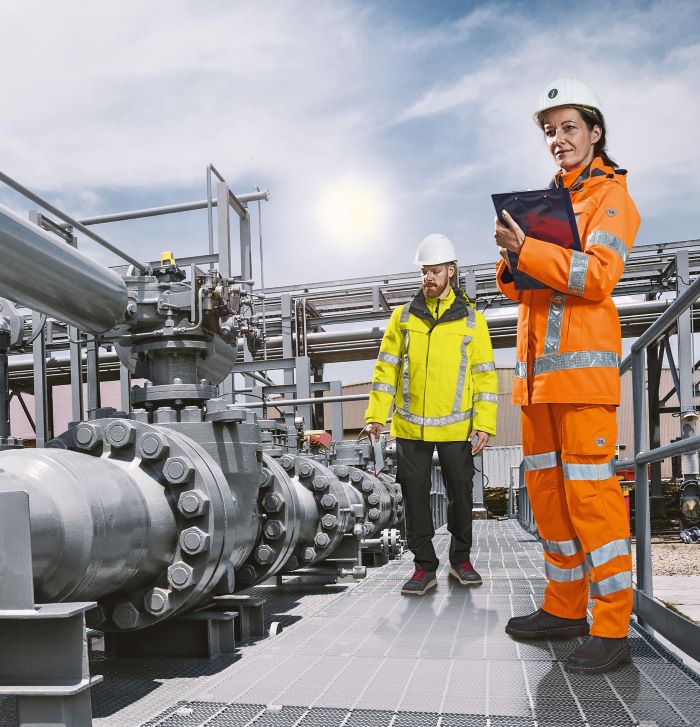
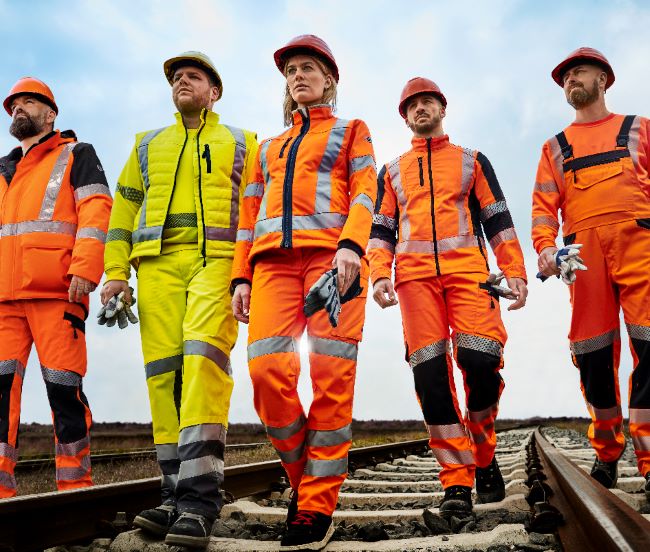
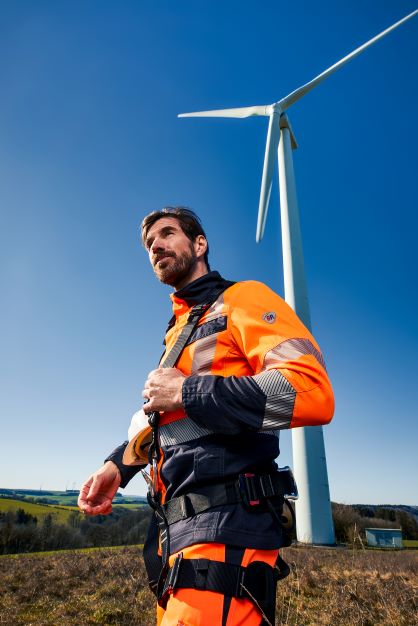
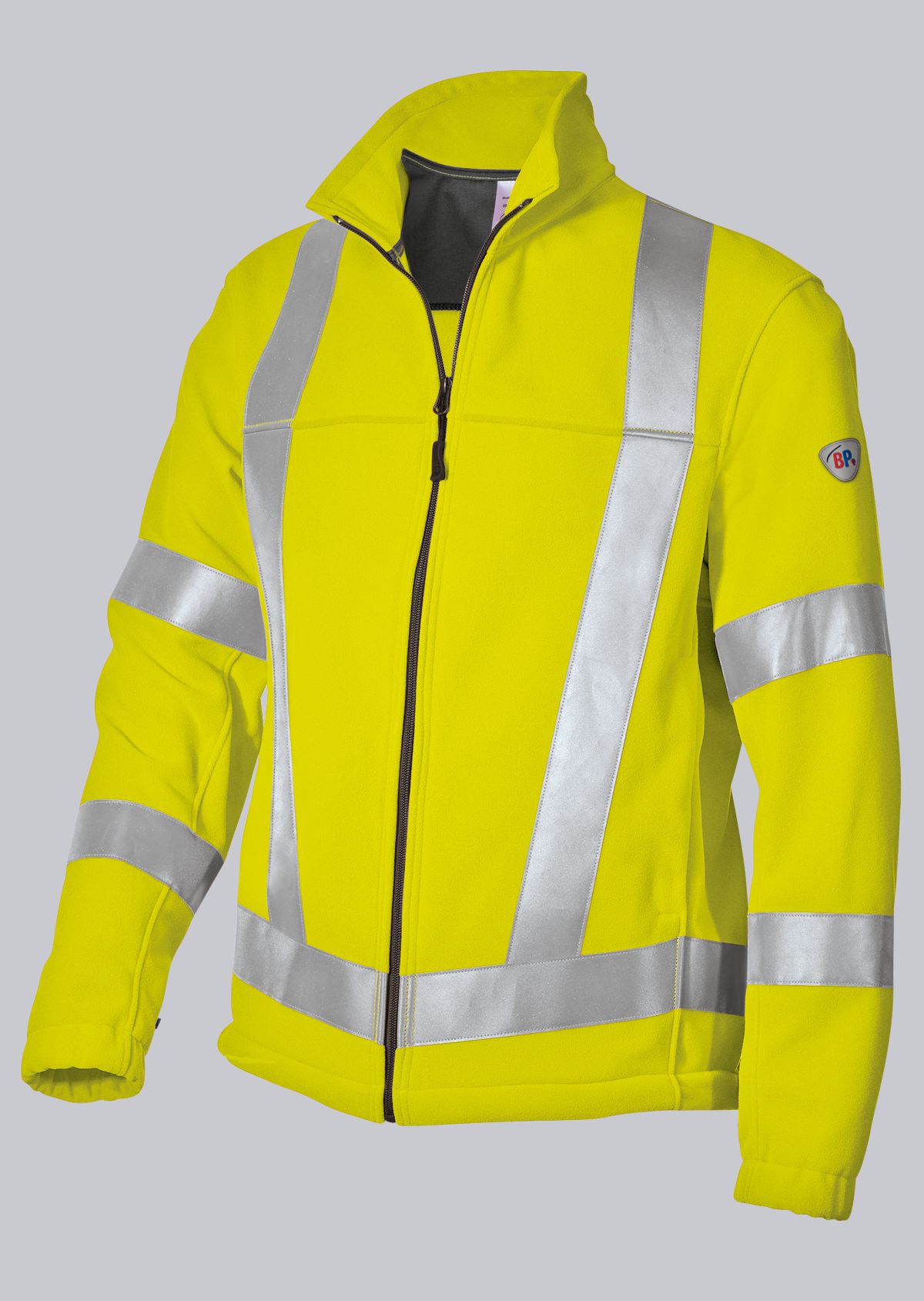
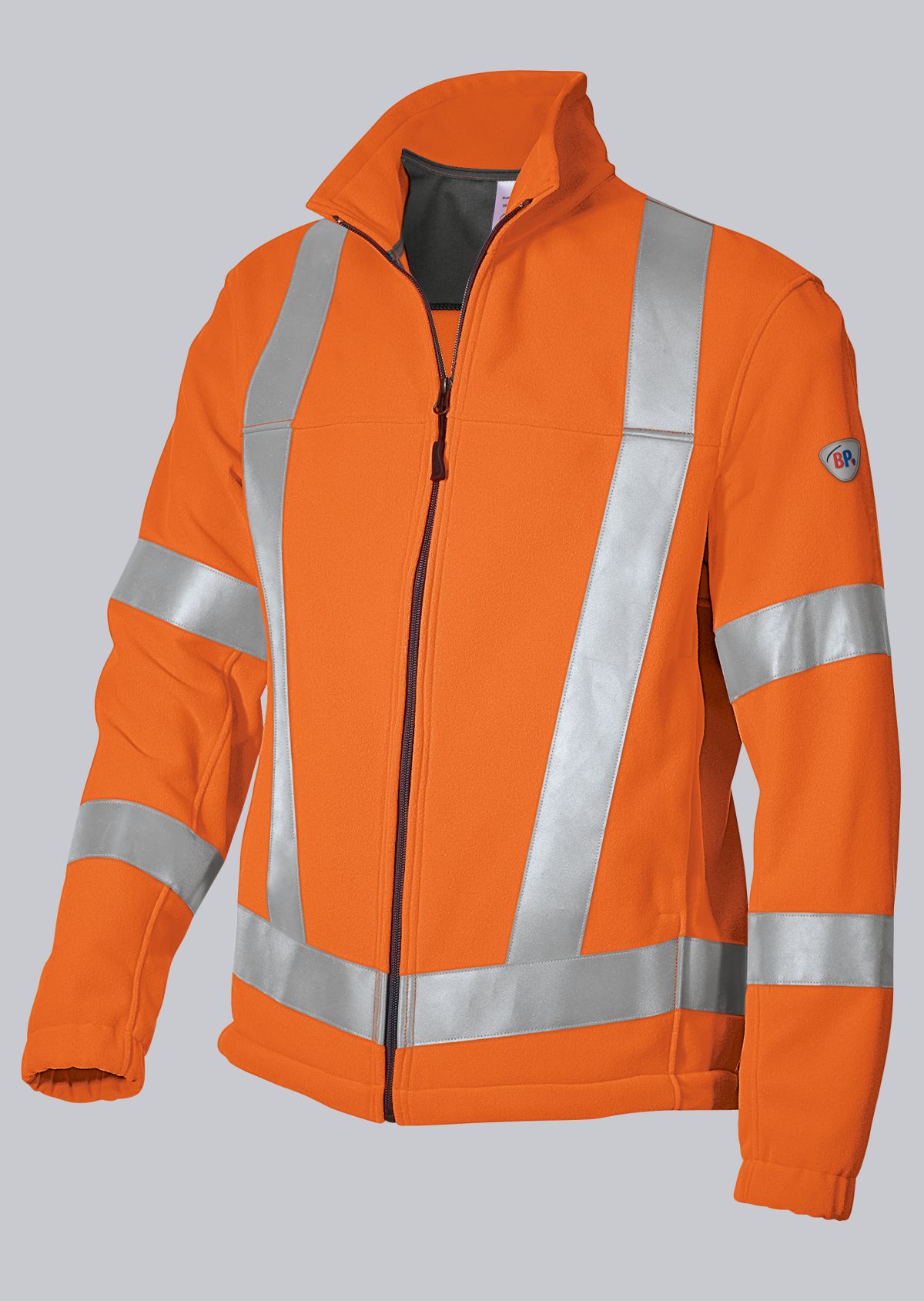
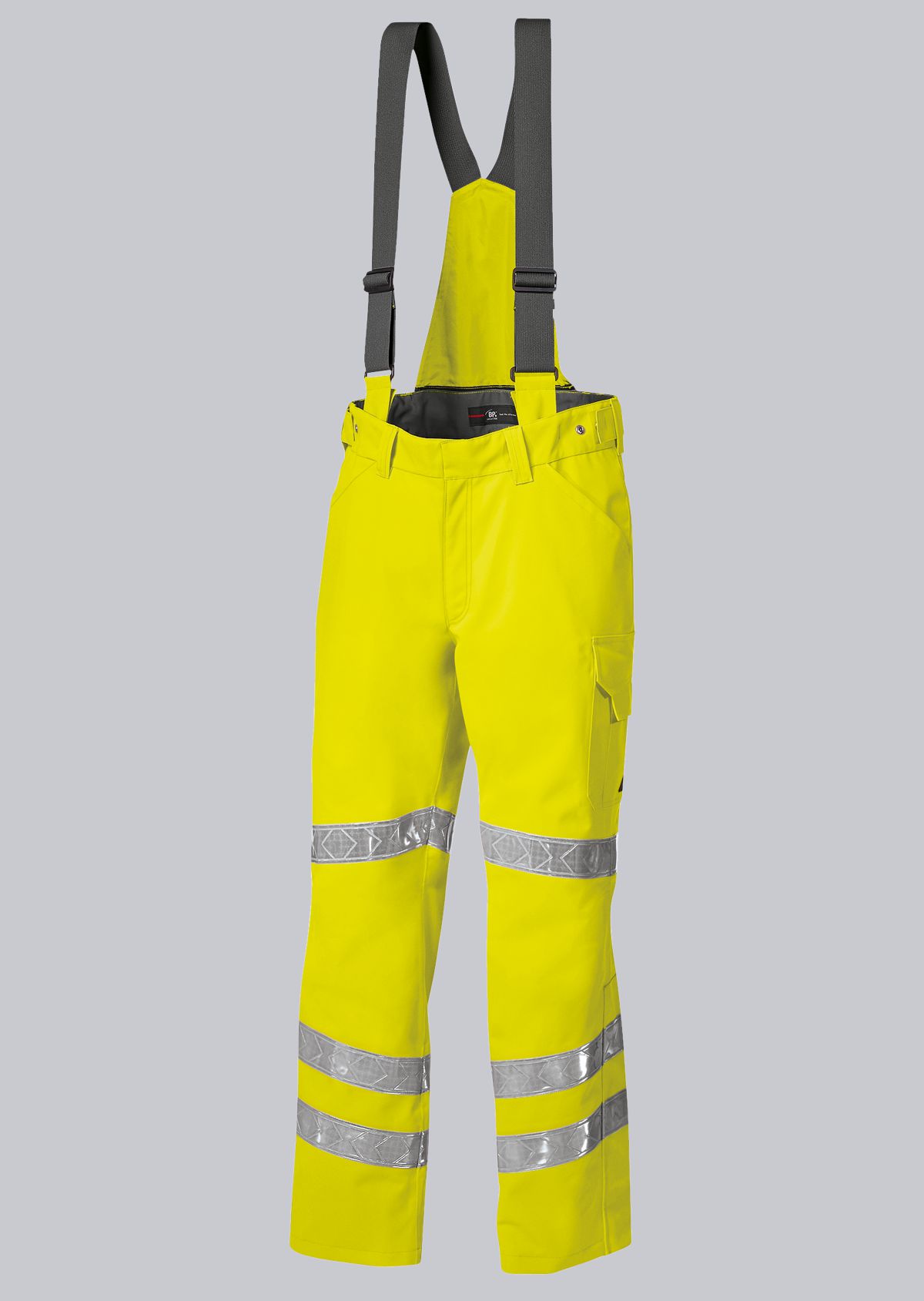
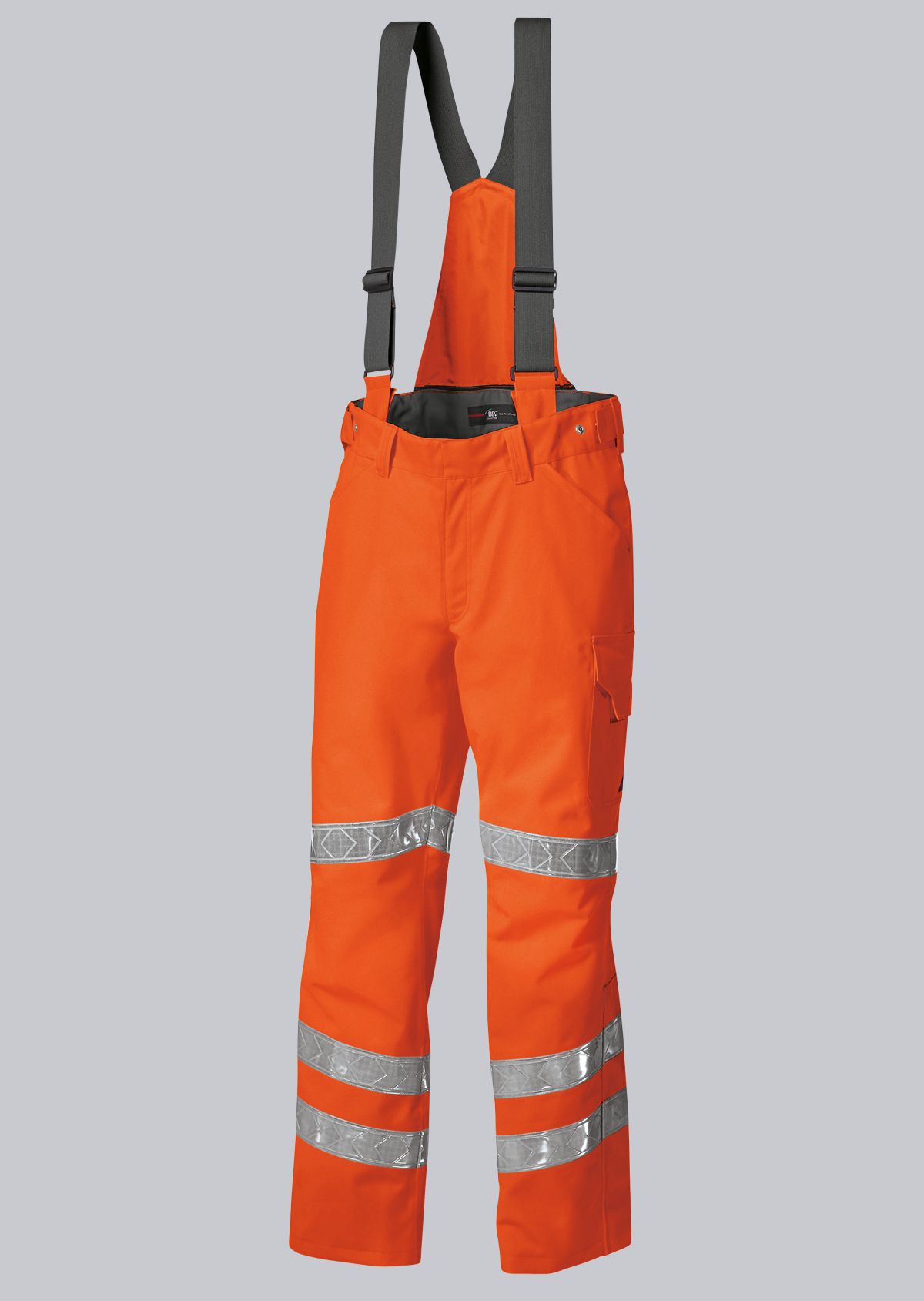
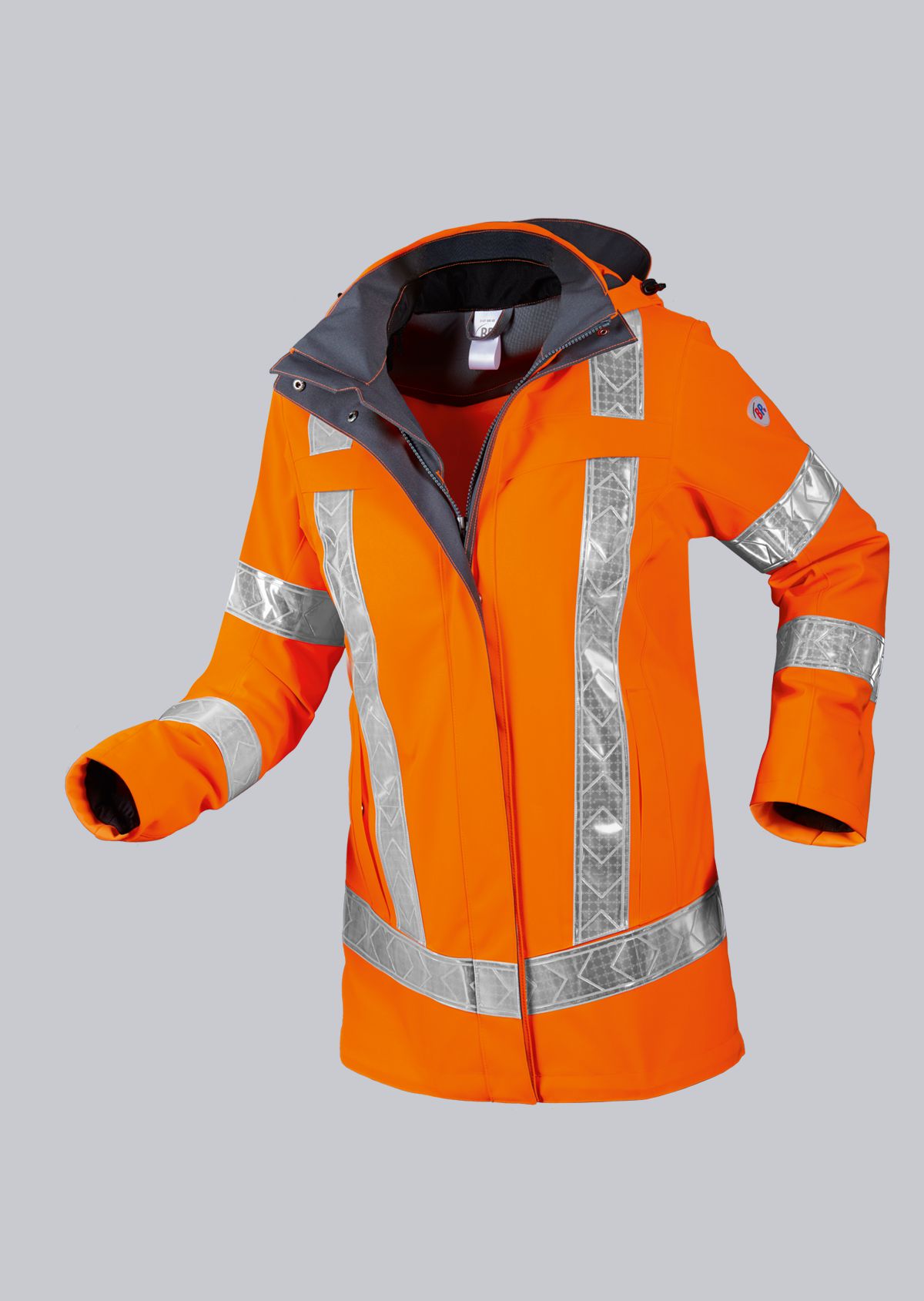
Protective clothing according to EN 14058
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective equipment here.


.jpg)
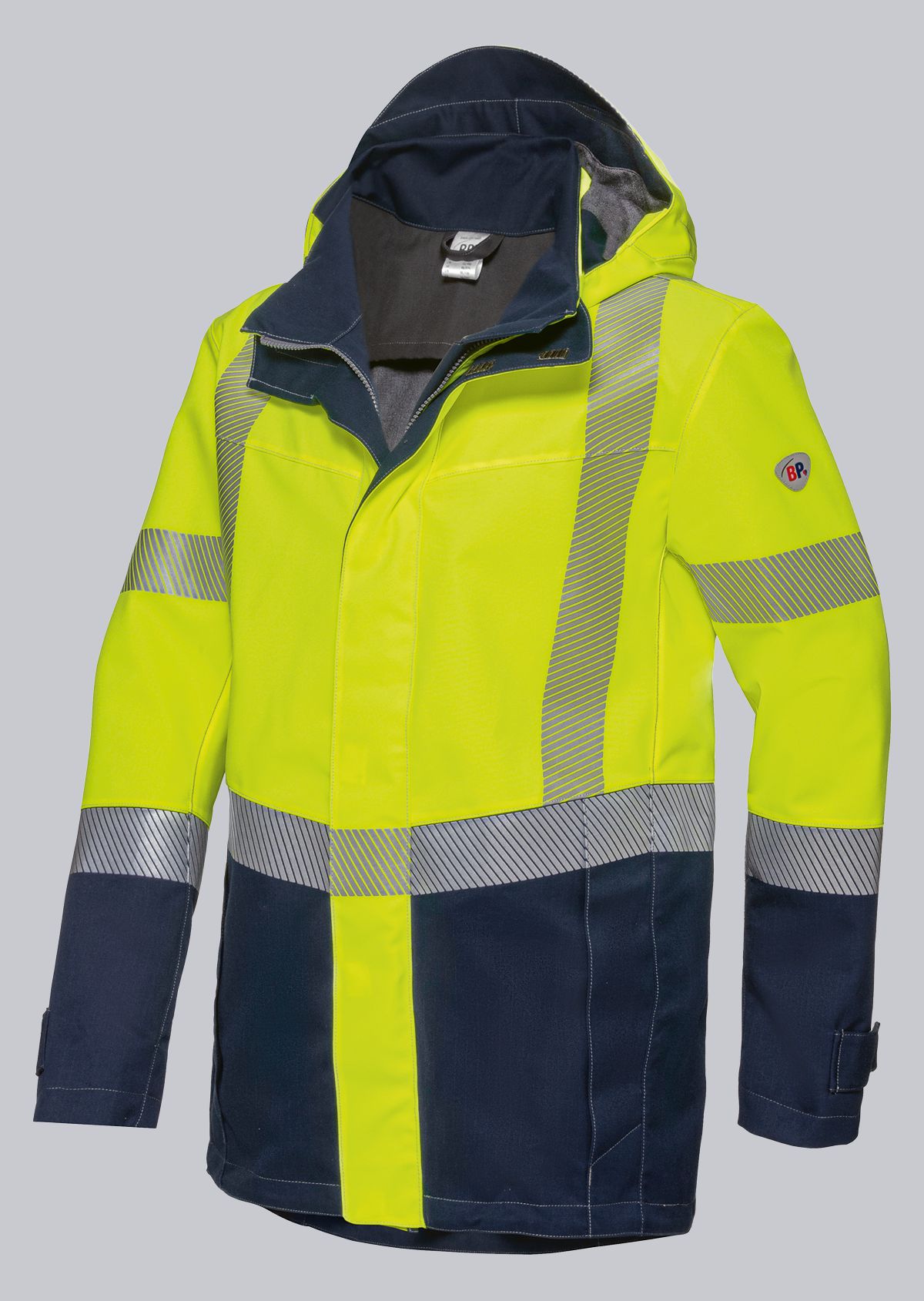
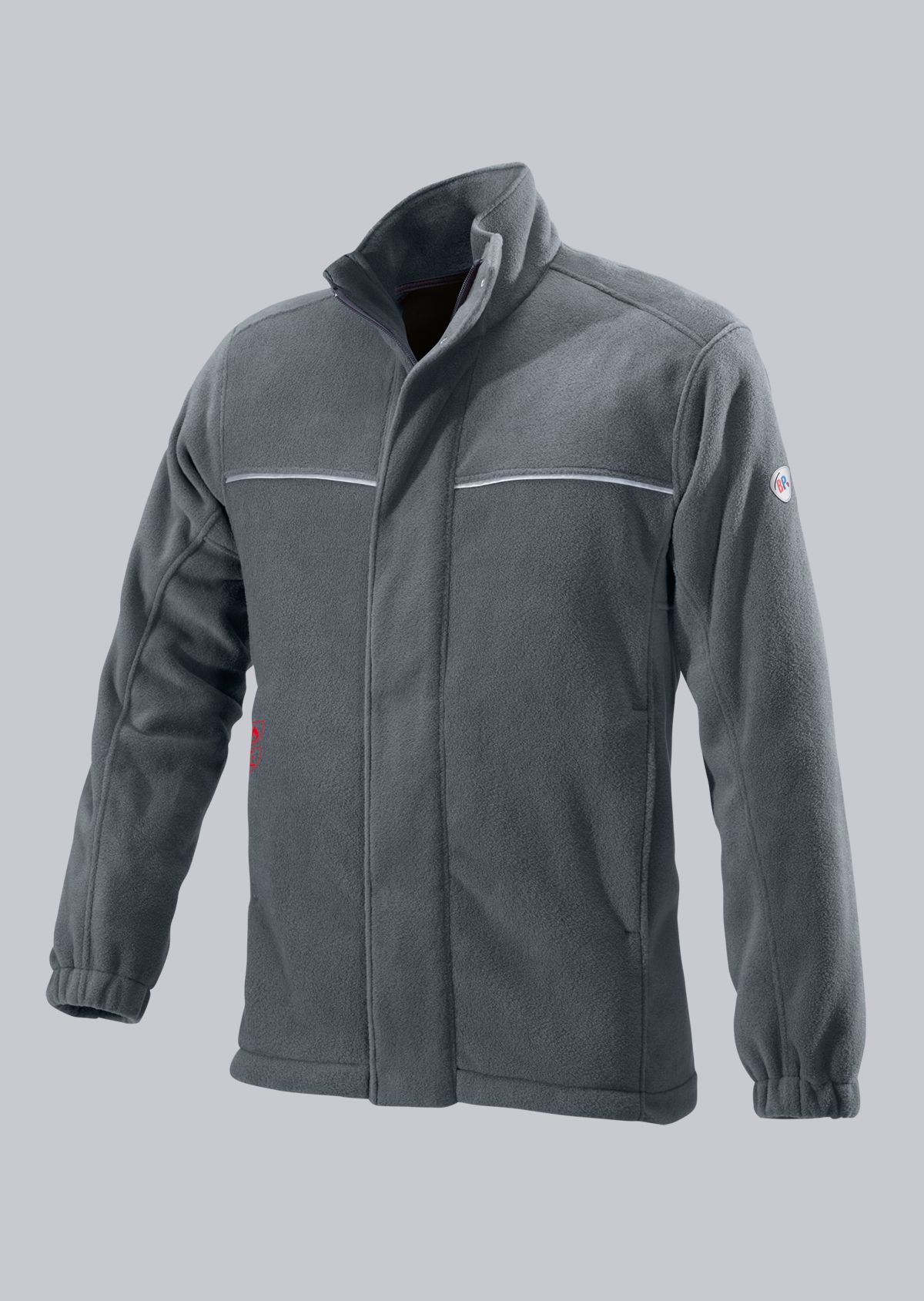
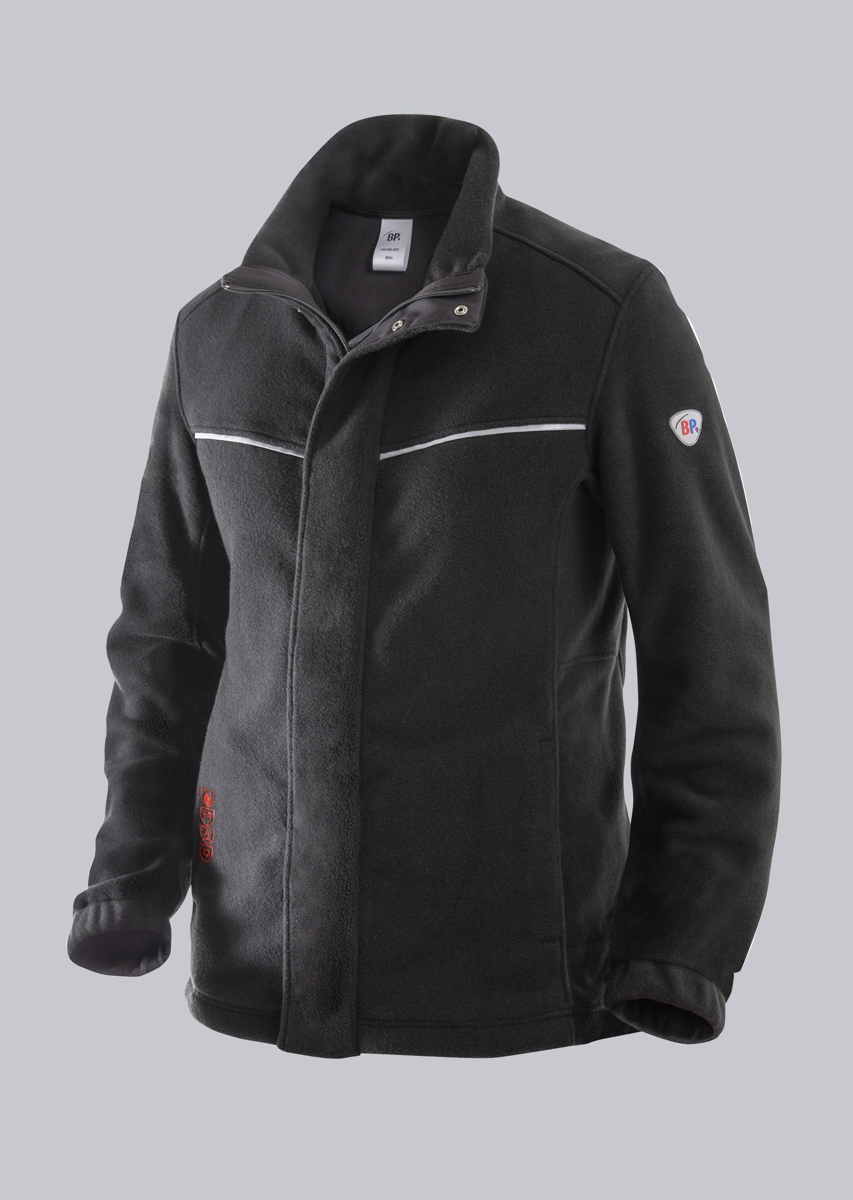
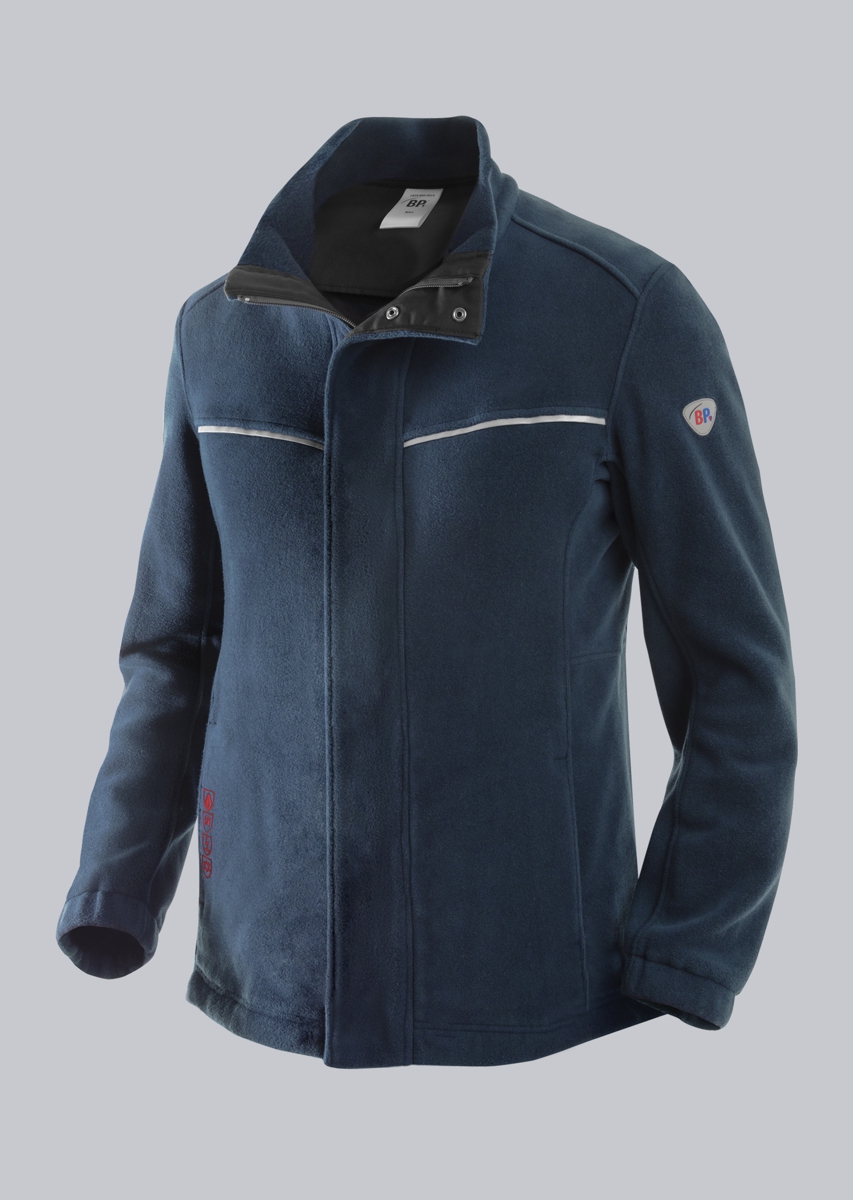
















.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
