
EN ISO 11611
EN ISO 11611 - Protective clothing
Protective clothing for welding and allied processes
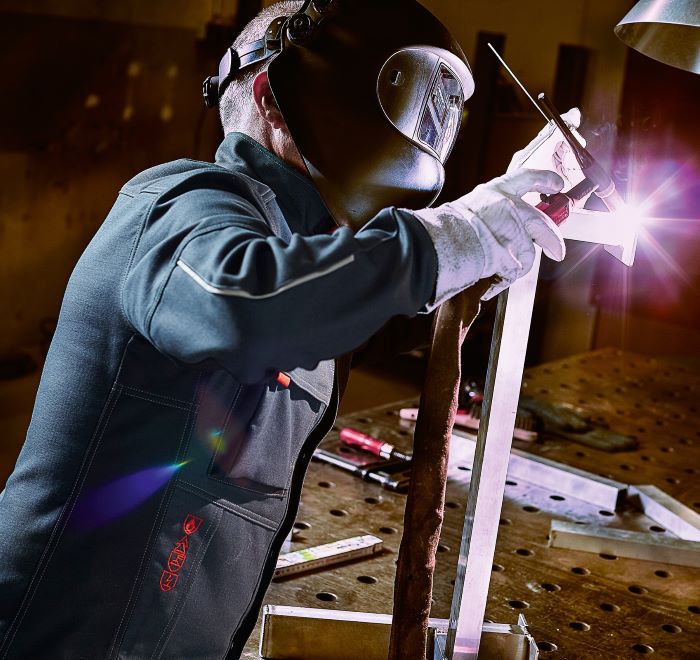
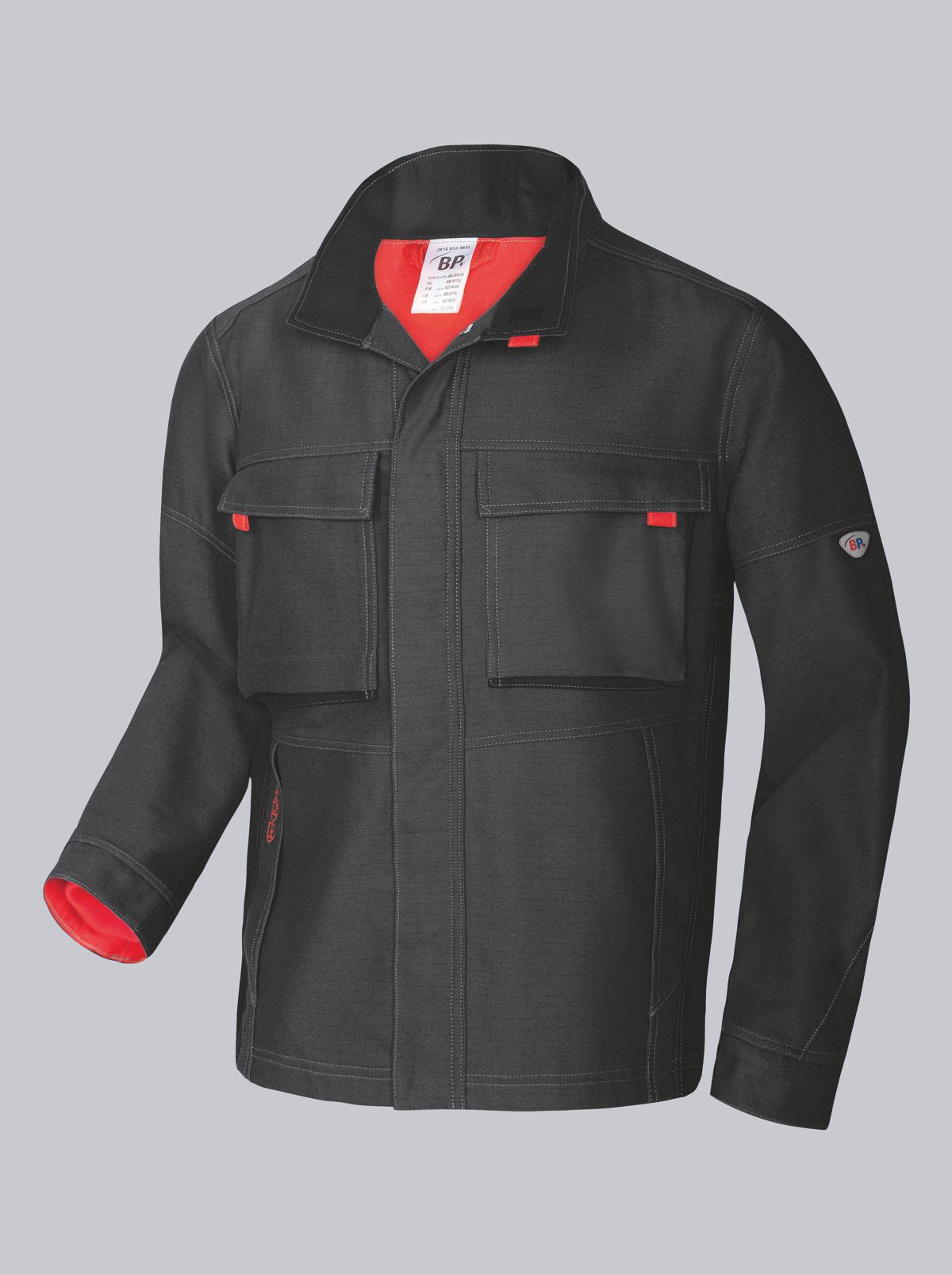
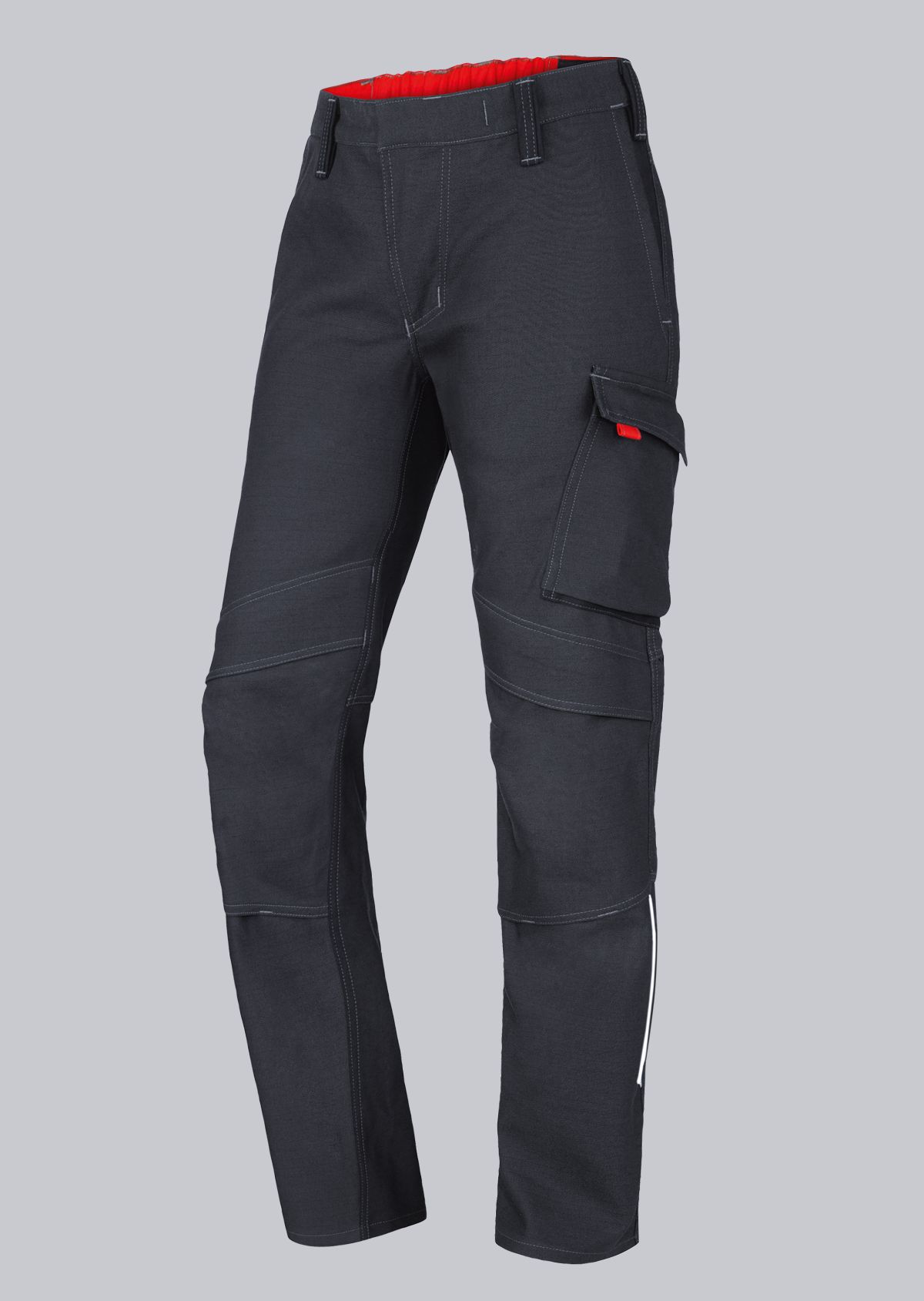
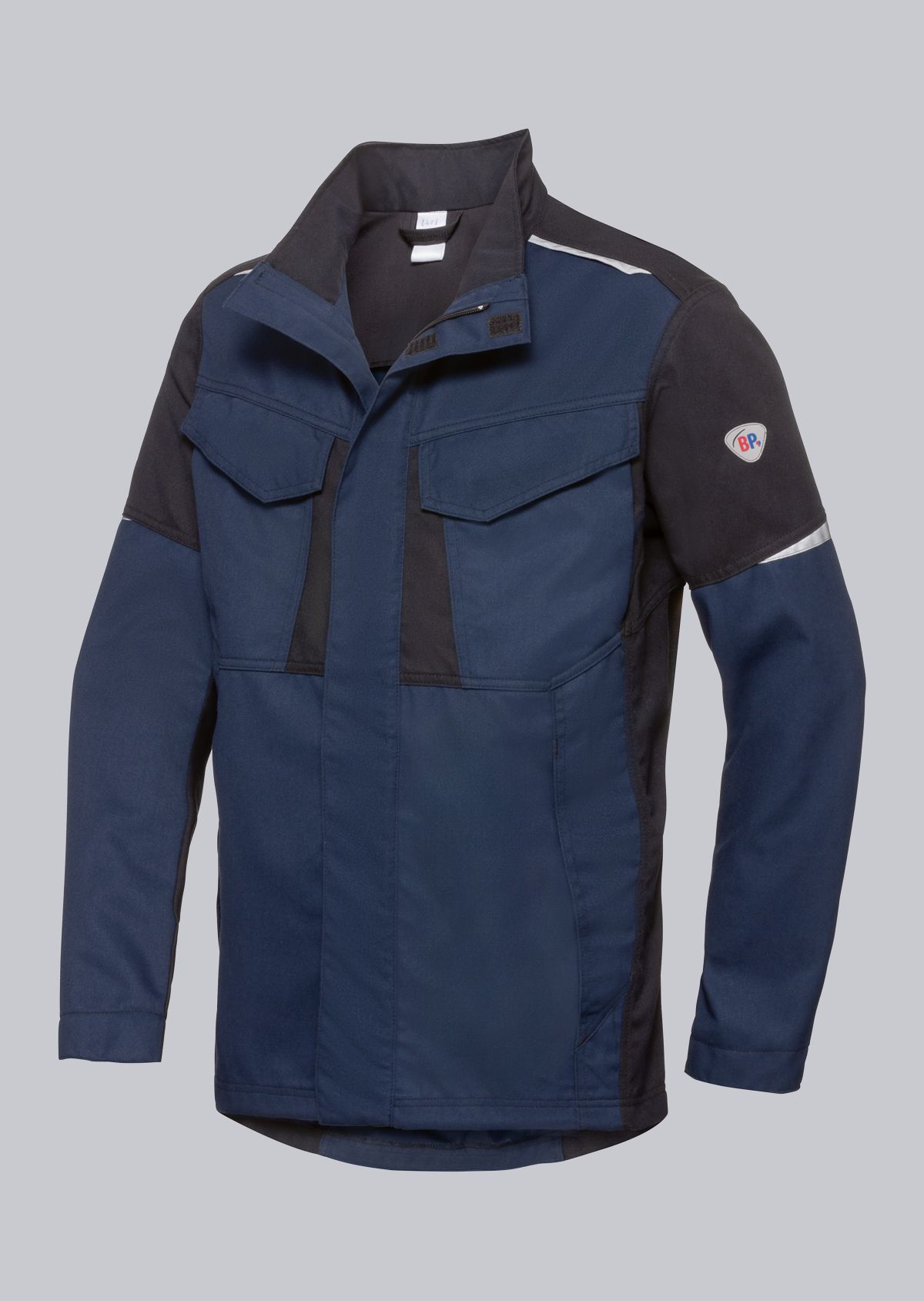
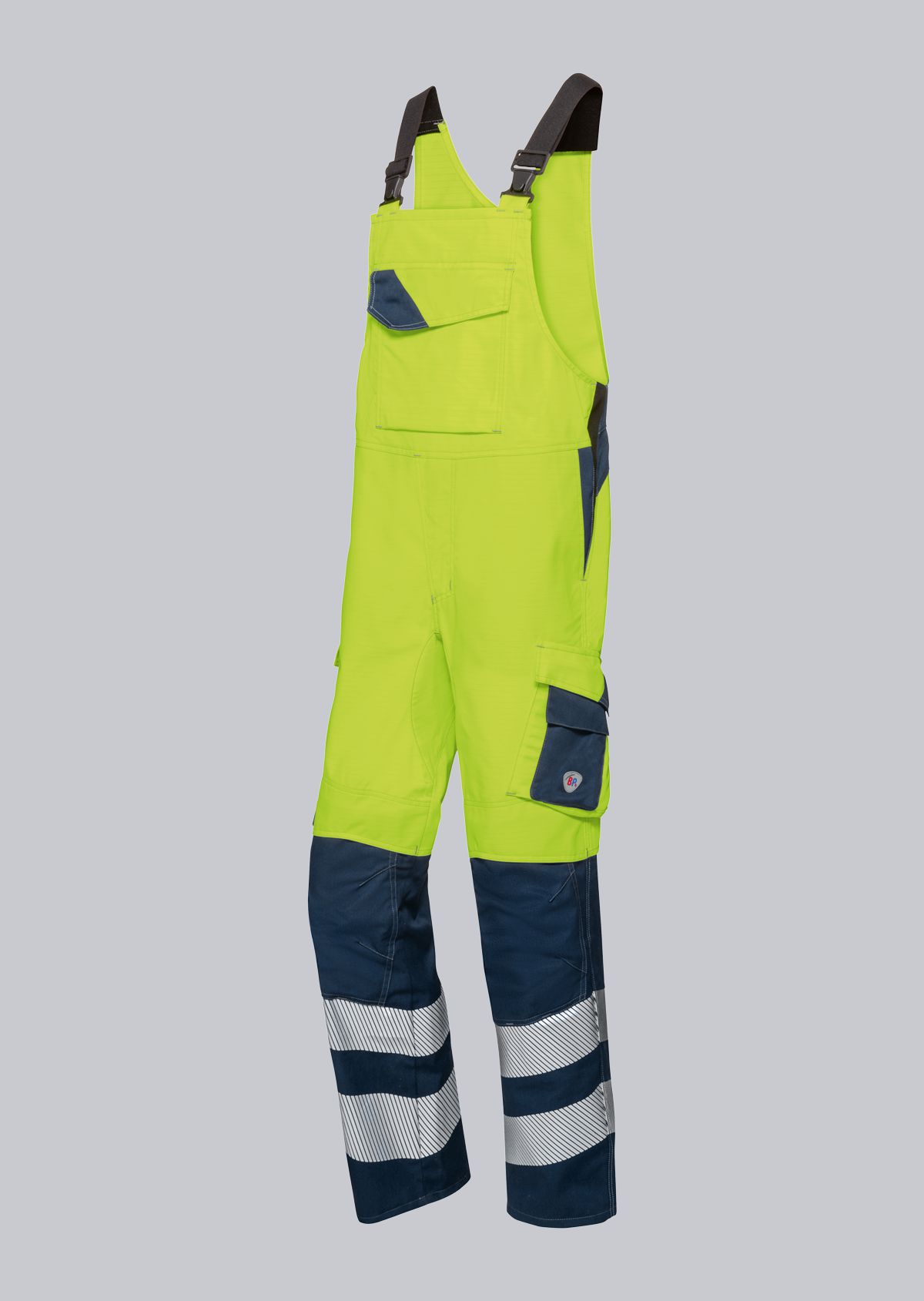
The EN ISO 11611 standard protects workers involved in welding and allied processes. It specifies the requirements for protective clothing designed to protect welders from the potential hazards that can occur during welding and related activities. This standard ensures that the workwear provides the necessary protection to minimise injuries and health risks while ensuring working comfort. In this article, we will take a closer look at the importance of the EN 11611 standard, its requirements and how it helps to ensure the safety of workers in these demanding work environments. Click here to go directly to welding protective clothing.
Important tips for welders
What do I need to consider when using protective welding clothing?
- All areas of skin not covered by the protective clothing must be protected by additional equipment such as protective bonnet, gloves, hose scarf, etc.
- Depending on the work task and welding position, it may also be necessary to wear additional leather aprons, leather gaiters.
- Protective clothing for welders must not be contaminated by oil, grease, oxygen, etc. When cleaning, care must be taken to ensure that the manufacturer's instructions are followed. This is the only way to ensure the effectiveness of the equipment.
- For the selection of protective clothing for welders for different welding activities, Annex A of EN ISO 11611:2015 "Guidance for the selection of the type of protective clothing for welders, Class 1 and 2" shall be used or referred to.
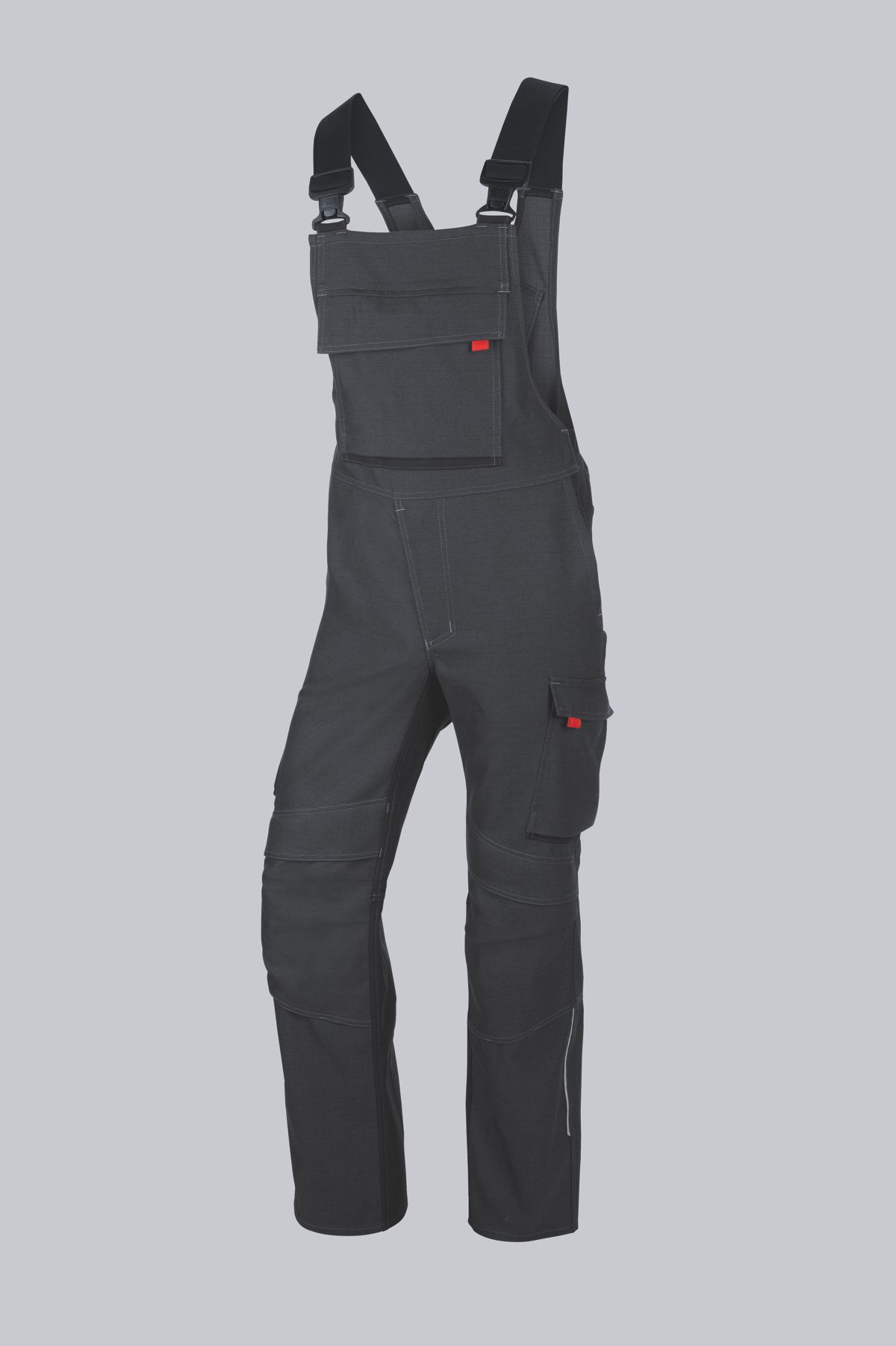
Design requirements for protective welding clothing:
- All pockets must be covered with flaps so that no metal splashes can fall into the pockets.
- Pocket flaps must be 2 cm wider than the opening width so that they cannot be pushed into pockets.
- Fasteners must not form folds where metal splashes can remain.
- The width adjustment on the cuffs must be on the underside of the sleeve.
- The angle of the trouser pockets must not exceed 10°.
- The jacket collar must be able to be fastened up to the top. No continuous metal parts (e.g. press studs) are permitted so that no thermal bridges are created.

TEAM EQUIPMENT REQUIRED?
You want to equip an entire team or company with PPE and need support in selecting and compiling protective clothing that conforms to standards?
CONTACT US

















.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)